Cron for Linux
The Cron job scheduler is a component of the Linux operating system. It is used to run server-side scripts according to a set schedule.
Starting with Passwork 5.1.0 there is a special script which is used to run the background tasks:
/var/www/app/tools/run-scheduled-tasks.php
It can be executed manually or set to run on the Cron scheduler.
We recommend that you first test the script in manual mode. To do this, run the script:
cd /var/www/app/tools/
php run-scheduled-tasks.php
Then, check the file at /var/www/app/logs/run-command.log for errors
Your user must have write access to the logs folder
Setting up Cron
Let's set up run-scheduled-tasks.php to launch every minute.
Open the Cron settings file:
crontab -e
Then add the line:
* * * * * php /var/www/app/tools/run-scheduled-tasks.php
And save the file.
Testing and troubleshooting
Open Passwork under an administrator's account and open the Background tasks page.
If everything was set up correctly, you will see a message that the scheduler is configured:
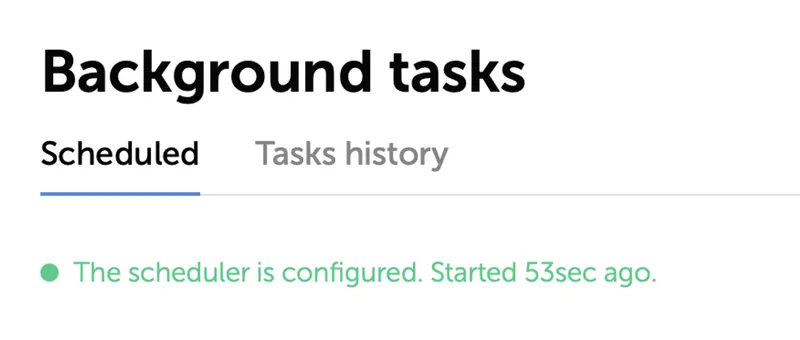
If you see a message that the scheduler is not configured, runtime errors can be found in the log file at /var/www/app/logs/run-command.log. You can forward it to our technical support if you need help with troubleshooting.
Setting up a script to run as non-root user
By default, Cron runs scripts as a root user. You can set up another user with limited privileges to increase security.
First, log in as a required user:
su - user
Run the script to make sure that everything works correctly under user:
cd /var/www/app/tools/
php run-scheduled-tasks.php
Check that user has write rights to the logs folder:
/var/www/app/logs/
If no errors show up, set up Cron for user:
# get back to root
exit
crontab -u user -e
Add the following line:
* * * * * php /var/www/app/tools/run-scheduled-tasks.php
And save the file.
Cron logs
To view the Cron log, use the following command:
journalctl -u crond

