Authorization configuration in Linux
Connecting and creating user in MongoDB
Connecting to the shell
Connect to the MongoDB shell:
- shell
mongosh
Creating user
Switch to the admin database:
- shell
use admin
Create a user by changing the login (user) and password (pwd):
- shell
db.createUser({
user: "adminuser",
pwd: "password",
roles: [
{ role: "root", db: "admin" }
],
passwordDigestor: "server"
})
The following characters are prohibited in the username and password as they may cause connection failures to MongoDB: . @ $ : % " ' / \ |
Enabling authorization and connecting Passwork
Enabling authorization in MongoDB
Edit the MongoDB configuration file to enable authorization by running the following commands in the shell to find its location:
- shell
var cmdLineOpts = db.serverCmdLineOpts();
print("config: " + cmdLineOpts.parsed.config);
Edit the obtained configuration file by modifying and adding the following lines:
- shell
security:
authorization: enabled
Example of the edited file
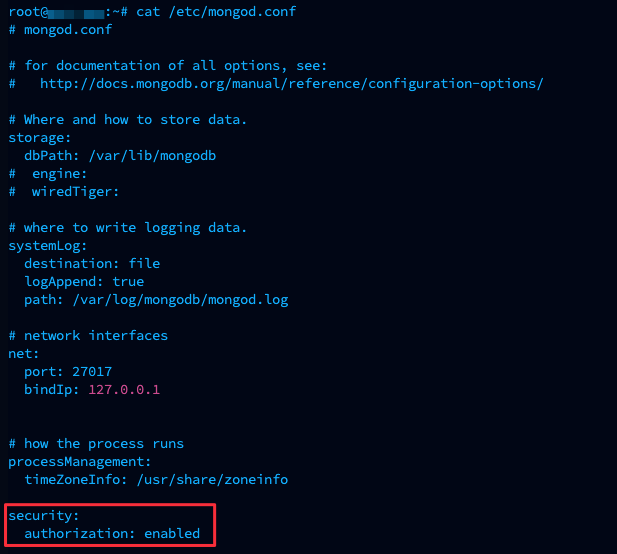
Note that indentation is a critical detail of the configuration file syntax.
Save the changes and restart the MongoDB service:
- shell
systemctl restart mongod.service
To verify, connect to the shell with authorization:
- shell
mongosh "mongodb://adminuser:password@localhost:27017"
Configuring and connecting Passwork with authorization
Edit the Passwork configuration file /var/www/init/config.env, specifying the username and password of the created user:
MONGODB_USERNAME=adminuser
MONGODB_PASSWORD=password
Save the changes and refresh the Passwork page to verify the connection with MongoDB authorization.

