Basic Cron commands
If you want to edit the Crontab file (a file containing instructions for executing scheduled jobs), enter the following command in the terminal:
crontab -e
The result will look like this:
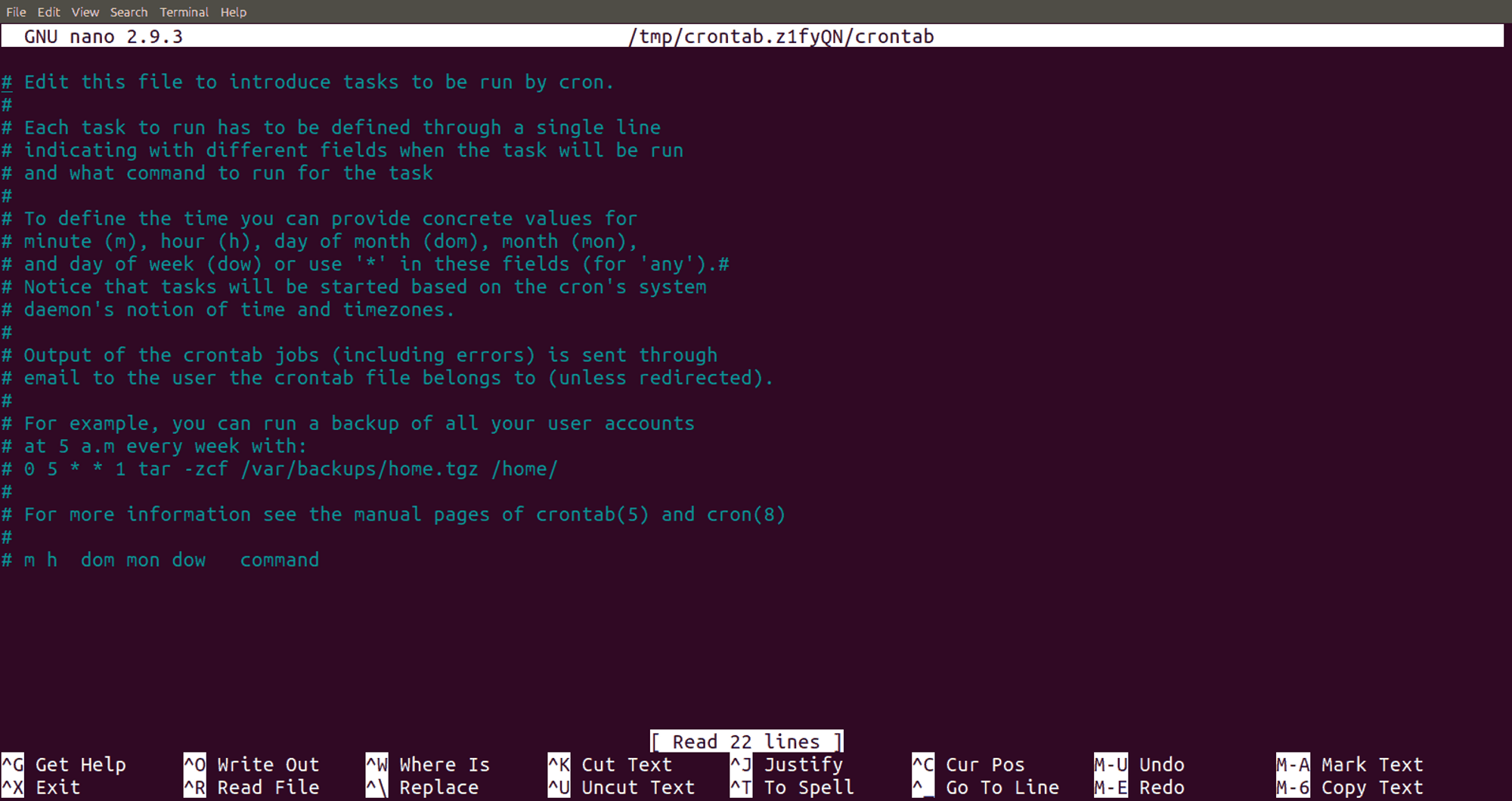
Most likely, the vi editor will open. Since this editor is often used when working with Cron, we recommend familiarizing yourself with the basic vi commands.
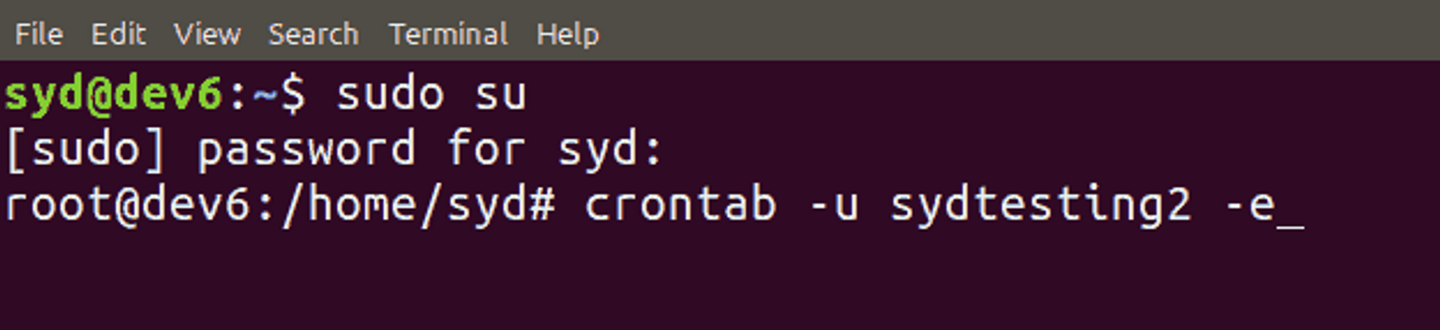
If you want to edit the crontab file of another user, use the command crontab -u username -e. Only superusers can edit other users' files, so you will need to enter sudo su before the command.
If you want to delete the current crontab file of the current user, enter the following command:
crontab -r
The command below is similar to the -r command, but it asks for confirmation before deleting the crontab file:
crontab -i
If you want to display the contents of the open crontab file, enter the following command in the terminal:
crontab -l
This command can also show whether you have crontab files. If no files have been created, the following message will be displayed:
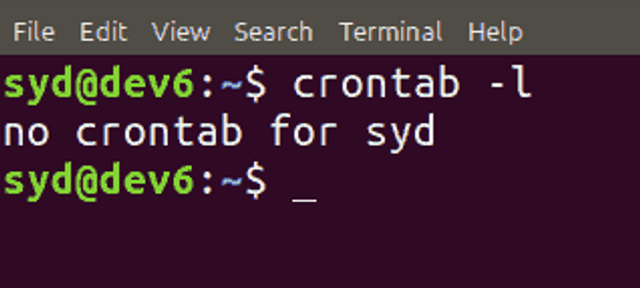
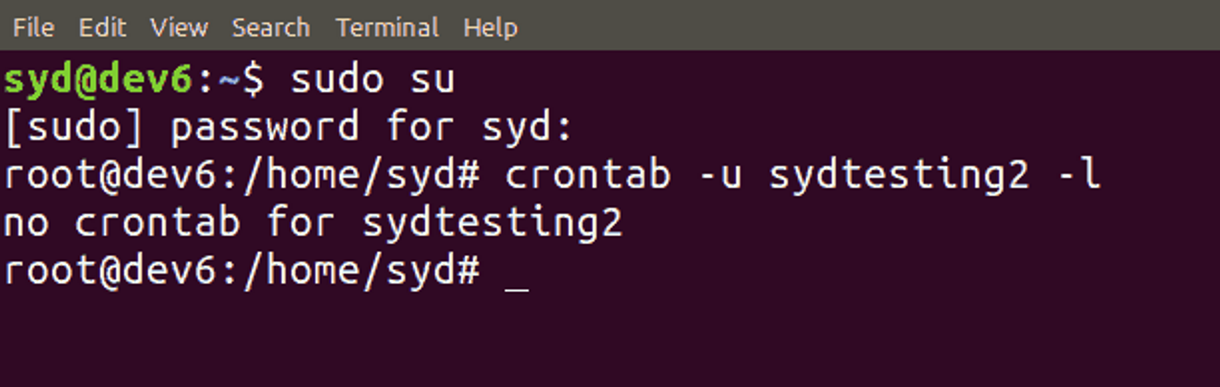
To view crontab files of other users, enter the following command as a superuser:
crontab -u username -l
Cron syntax
A crontab file consists of two parts: the schedule and the command. The command looks like this:
* * * * * /bin/sh backup.sh
For example,
- * * * * /bin/sh backup.sh runs the backup every minute.
- 30 18 * * * rm /home/sydtesting/tmp/* means that tmp files will be deleted from /home/sydtesting/tmp every day at 18:30.
The Crontab file has five fields. Each field is represented by an asterisk and defines the date and time of the task that should be executed regularly.

- Minutes — the minute of the hour when the command will be run (from 0 to 59).
- Hours — the hour when the command will start (from 0 to 23).
- Day of month — on which day of the month the command should run (from 1 to 31).
- Month — in which month the command will be executed (from 1 to 12).
- Day of week — on which day of the week the command should run (from 0 to 6, 0 — Sunday).
Certain symbols also have meaning. Use:
- Asterisk (*) to specify scheduling parameters.
- Comma (,) to specify two or more execution time options.
- Hyphen (-) to set a range of execution times.
- Slash (/) to create specified time intervals within a certain range.
- Last (L) to specify the last day of the week in a given month. For example, 3L means the last Wednesday.
- Weekday (W) to specify the nearest weekday to a given time. For example, 1W means the script will run on the nearest weekday to the first day; if the 1st is Sunday, the command will run on Monday (the 2nd).
- Hash (#) to specify the day of the week in the month field (from 1 to 5). For example, 1#2 means the second Monday.
- Question mark (?) to select a specific day to run the script. For correct operation, you need to specify either the day of the month or the day number — you cannot specify both simultaneously. This symbol allows leaving one value empty.
Examples
Note that the command output is automatically sent to the local email. If you do not want to receive these emails, add >/dev/null 2>&1 to the syntax, as shown in the example:
0 5 * * * /root/backup.sh >/dev/null 2>&1
If you want the output to be sent to another email, you can add MAILTO, followed by the email address. For example:
MAILTO="[email protected]"
0 3 * * * /root/backup.sh >/dev/null 2>&1
More syntax examples:
| Expression | Action |
|---|---|
| 0 0 * * * /bin/sh backup.sh | Perform database backup at midnight once a day. |
| 0 6,18 * * * /bin/sh backup.sh | Perform database backup twice a day at 6 AM and 6 PM. |
| 0 */6 * * * /scripts/monitor.sh | Perform monitoring every six hours. |
| */10 * * * * /home/user/script.sh | Run a cron job for the script file located in the home directory every 10 minutes. |
| 0 * 20 7 * /bin/sh backup.sh | Run database backup every hour on July 20th. |
| 0 0 * * 2 * /bin/sh | Run database backup at midnight every Tuesday. |
| * * * 1,2,5 * /script/script.sh | Run the command in January, February, and May. |
| 10-59/5 5 * * * /home/user/script.sh | Run the command every 5 minutes at 5 AM, starting from 5:10 AM. |
| 0 8 1 */3 * /home/user/script.sh | Run the command quarterly on the 1st day at 8 AM. |
| * * * * * /scripts/script.sh; /scripts/scrit2.sh | To schedule multiple jobs in one cron job. |
| @reboot /scripts/script.sh | To run a specific task every time the system starts. |
| 0 0 1 * * /home/user/script.sh | Run the command on the first day of every month. |

