From smartphones to automobiles, almost every device is equipped with Bluetooth technology nowadays. Many people use it every day while connecting to headphones, sending files, or making remote calls in their cars. However, most people are unaware that using Bluetooth carries a number of risks when it comes to your privacy and safety.

What is Bluetooth?
Bluetooth technology is a standard for creating a local network that allows neighboring devices to exchange data wirelessly. In other words, you can use Bluetooth to transfer data between devices such as your phone and headphones without the use of a cable. Bluetooth is widespread and free to use, that’s why it is so popular with device creators and consumers.
Bluetooth was invented in 1994 by Ericsson — the telecommunications equipment manufacturer. Now, you can find this technology in almost every electrical device around the world. Even smart household appliances are equipped with Bluetooth nowadays, so you can send instructions to your refrigerator or vacuum cleaner remotely.
Bluetooth hacking
Of course, as with most standards, Bluetooth has its disadvantages and security vulnerabilities. Bluetooth allows devices to communicate with one another across short distances and for a limited time. As a result, most Bluetooth hackers focus on getting close to a target and carrying out the assault in a short amount of time. Particularly in areas where people tend to linger around. There are a number of places that pose a great amount of danger to your devices. For example, cafes, the underground during rush hour and on the bus.
However, when the attacker’s target moves out of range, it could stop the attack and ruin the hacker’s plans. It's worth noting that some attacks can be launched from hundreds of meters away. So moving a few steps isn't the same as being out of range.
Some hackers are also able to control your device for under 10 seconds using Bluetooth. Even more concerning is the fact that hackers can accomplish this without engaging with the user.
There are a variety of Bluetooth hacking techniques:
1. Bluejacking
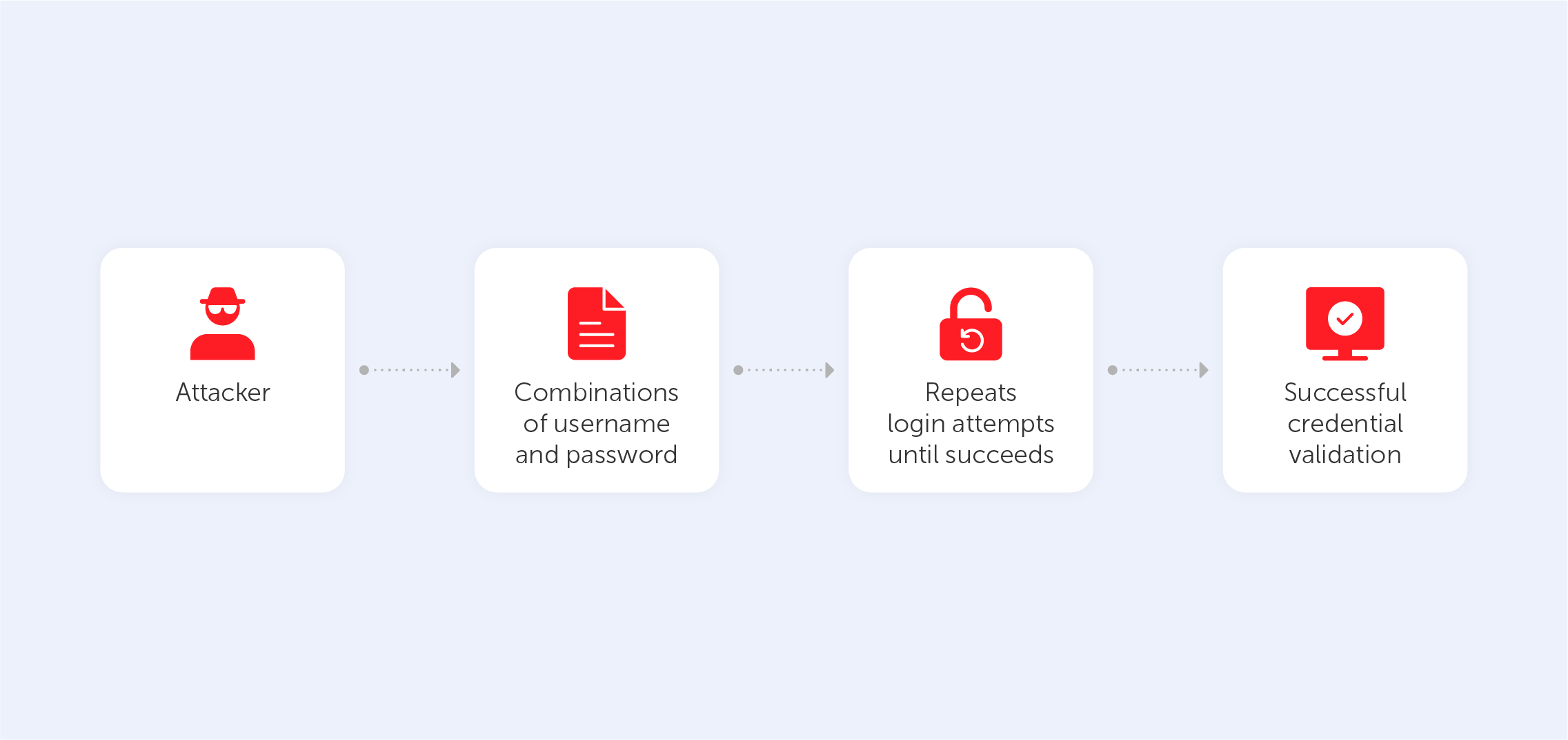
This type of cyberattack on Bluetooth connection lies in sending spam messages via Bluetooth. One Bluetooth-enabled device hijacks another and sends spam messages to the hijacked device. First of all, this can be annoying to get such spam. But if you click it and accept files from an unknown device, you may get into big trouble. The message may contain a link that will lead to a website that is designed to steal your personal information and compromise you.
2. Bluesnarfing
This type of attack is similar to the previous one but much more detrimental to your privacy. During these hijacking attempts, hackers can not only send spam messages to one’s phone, but also collect some private information like chat messages, photos, documents, or even credentials from the victim’s device. All of this will be used to compromise you or for extortion attempts.
3. Bluebugging
This is the last and the most dangerous type of Bluetooth hijacking. Hackers use your device to establish a secret Bluetooth connection. This connection is then used to acquire backdoor access to your device. Once inside, they can monitor your activities, gain your personal information, and even use your personality on your device's apps, including those used for online banking. This type of assault is known as blue bugging since it resembles bugging a phone. Once hackers get access and complete control over the phone, they get the opportunity to make phone calls themselves and listen in on every phone conversation.
Bluetooth security concerns
If you think that the direct invention of hackers is the only danger that Bluetooth presents, we have some bad news for you. Many apps including popular ones such as Google or Facebook can monitor the location of users through the use of Bluetooth technology.
By switching on Bluetooth, you enable the transmission of information, but you also enable your device to catch adjacent Bluetooth signals. Thus, Bluetooth signals are used by app developers to pinpoint your location. So, the IT companies that develop apps can find out the information about your location wherever you go and keep track of your everyday activities. The most terrifying aspect here is that Bluetooth enables extremely precise tracking. The good thing is that most app creators write that “the usage of their apps requires Bluetooth utilization” in their privacy statement. Unfortunately, the majority of consumers do not read the privacy statements of the apps they use, so they automatically accept all the requirements and rules of the new app.
To protect yourself from activity and location tracking, you should read each app’s privacy policies and not use apps that require Bluetooth. If you determine that some of the apps you regularly use are requiring Bluetooth, you can disable the location tracking function for them.
What do we need to do to safeguard our Bluetooth connections?
In mentioning all of the risks associated with the use of Bluetooth, we have to give you some advice regarding the safeguarding of your devices.
1. Make your Bluetooth device non-discoverable. This can be done in your device’s settings.
2. Do not send any sensitive information via Bluetooth as it can be caught by intruders.
3. Do not accept any files or messages from unknown devices via Bluetooth, especially in crowded places.
4. Always turn your Bluetooth off after using it to prevent unwanted connections and breaches.
5. Don’t share anything via Bluetooth in crowded places, even if you want to connect to your friend’s device.
6. Install some security patches to protect your device and stop any possible tracking via Bluetooth.
Conclusion
Bluetooth is a common and useful technology that is used in almost every device due to its convenience and fast connection. But the simplicity of its technology leads to several flaws, which is why Bluetooth can’t be named a very secure standard. Nevertheless, most people cannot avoid using this technology — it’s just too widespread. To keep your device safe, we recommend following the aforementioned security rules.