Alma/Rocky/CentOS
Passwork installation instructions for OS:
- CentOS 8 Stream, Alma Linux 8, Rocky Linux 8.
- CentOS 9 Stream, Alma Linux 9, Rocky Linux 9.
The instructions use switchable code blocks to separate commands according to the operating system versions.
1. Minimum system requirements
Passwork is not demanding on system resources, and the required number of servers depends on the number of active users, the volume of stored data, and system fault tolerance requirements.
Please review the full system requirements.
If the server has 2-4 GB of RAM, we recommend enabling a SWAP file.
2. Basic actions before installation
Obtain root privileges and update the local package database:
- shell
sudo -i
dnf makecache
Install the Apache2 web server and the data transfer utility curl:
- shell
dnf install -y httpd unzip curl zip jq
Replace the DocumentRoot location in the Apache configuration:
- shell
sed -i 's|^DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"|DocumentRoot "/var/www"|' /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Start the httpd.service service:
- shell
systemctl start httpd.service
Enable the service to start automatically:
- shell
systemctl enable httpd.service
2.1 Installation and basic configuration of Firewalld
Install the dynamic firewall management service Firewalld:
- shell
dnf install firewalld -y
Start the firewalld.service service:
- shell
systemctl start firewalld.service
Enable the service to start automatically:
- shell
systemctl enable firewalld.service
Add the HTTPS protocol to the list of allowed services in the Firewalld configuration:
- shell
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
Apply changes to the Firewalld configuration:
- shell
firewall-cmd --reload
2.2 Disabling SELinux and rebooting the OS
Edit the configuration file /etc/selinux/config:
- shell
nano /etc/selinux/config
Change the SELINUX parameter value from enforcing to disabled:
- shell
SELINUX=disabled
Save changes (Ctrl+O) and exit (Ctrl+X). Reboot the system to apply SELinux changes:
- shell
reboot
3. PHP installation
Install the EPEL package (epel-release) and package management utilities yum (yum-utils):
- shell
dnf -y install epel-release yum-utils
Download and install the latest EPEL repository:
- OS 9
- OS 8
dnf install -y https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm
dnf install -y https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
Download and install the repository providing access to PHP versions:
- OS 9
- OS 8
dnf install -y https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-9.rpm
dnf install -y https://rpms.remirepo.net/enterprise/remi-release-8.rpm
Enable the PHP 8.3 module from the REMI repository:
- shell
dnf module enable php:remi-8.3
Install PHP and additional extensions:
- shell
dnf install -y php-cli php-fpm php-curl php-devel php-pear php-gd php-intl php-ldap php-bcmath php-mbstring php-mysqlnd php-opcache php-pgsql php-soap php-zip php-sqlite3 php-xml
Change the amount of RAM available for executing PHP scripts:
- shell
sed -i 's/^memory_limit\s*=.*/memory_limit = 256M/' /etc/php.ini
It is recommended to increase the memory_limit parameter from 256M to 512M or higher if a large number of users are expected to use Passwork.
Ensure the php-fpm service is running:
- shell
systemctl status php-fpm
Start and enable the service if it is stopped:
- shell
systemctl start php-fpm
systemctl enable php-fpm
3.1 Installing PHP MongoDB driver
Install the PHP MongoDB driver:
- shell
pecl install mongodb
Press Enter to accept the default build options.
Create a configuration file to load and enable PHP MongoDB:
- shell
echo "extension=mongodb.so" | tee /etc/php.d/20-mongodb.ini
4. MongoDB database installation
Create a file to add the MongoDB repository to the yum package manager:
- shell
nano /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-7.0.repo
Place the following content into the file:
- OS 9
- OS 8
[mongodb-org-7.0]
name=MongoDB Repository
baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/9/mongodb-org/7.0/x86_64/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://pgp.mongodb.com/server-7.0.asc
[mongodb-org-7.0]
name=MongoDB Repository
baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/8/mongodb-org/7.0/x86_64/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://pgp.mongodb.com/server-7.0.asc
Install MongoDB:
- shell
dnf install mongodb-org -y
Start the mongod.service service:
- shell
systemctl start mongod.service
Enable the service to start automatically:
- shell
systemctl enable mongod.service
5. Obtaining and configuring Passwork
Online
Obtain the script:
- wget
- curl
wget https://repos.passwork.pro/repository/linux/scripts/passwork.sh
curl -O https://repos.passwork.pro/repository/linux/scripts/passwork.sh
The Passwork installation script must not be located in the directory with the application server files.
Assign execution permissions to the script:
chmod +x passwork.sh
By default, the passwork.sh script will:
- Create a hidden
.script_envfile in the current directory; - Create a
passwork_archivedirectory for Passwork backups; - Obtain the latest available Passwork version, signature, and public key;
- Install the previously obtained archive to
/var/www/
To use a non-standard installation path, disable certificate verification, or change behavior, you can use script launch parameters.
Run the script:
sudo ./passwork.sh
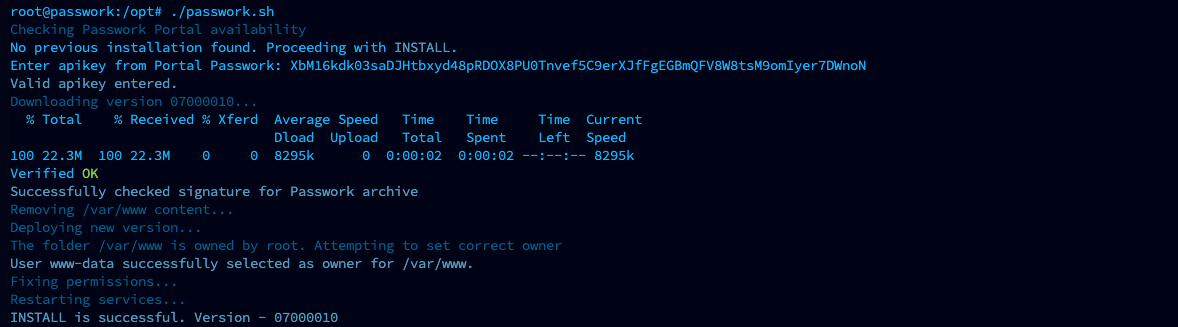
On the first run, the script will request an API key and perform basic environment checks:
Example of successful script execution:
Offline
Obtain the script on another machine with Internet access:
- wget
- curl
- PowerShell
wget https://repos.passwork.pro/repository/linux/scripts/passwork.sh
curl -O https://repos.passwork.pro/repository/linux/scripts/passwork.sh
(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("https://repos.passwork.pro/repository/linux/scripts/passwork.sh", "$PWD\passwork.sh")
Or obtain the passwork.sh script manually using the link
The Passwork installation script must not be located in the directory with the application server files.
Assign execution permissions to the script:
chmod +x passwork.sh
Before running passwork.sh, you need to:
- Obtain Passwork version 7 from our Customer Portal (mandatory);
- Place it in the launch directory or use the
--inputargument to specify the location (mandatory); - Obtain the archive signature and public key of Passwork (optional if using the
--skipargument).
By default, the passwork.sh script will:
- Create a
passwork_archivedirectory for Passwork backups; - Extract the Passwork archive;
- Install the previously obtained archive to
/var/www/
To use a non-standard installation path, disable certificate verification, or change behavior, you can use script launch parameters.
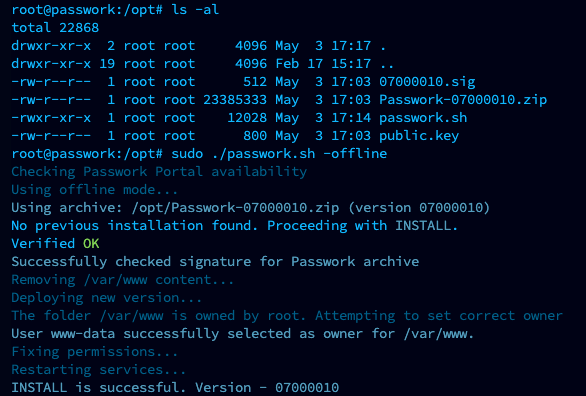
After preparation, run the passwork.sh script:
sudo ./passwork.sh -offline
Example of successful offline script execution:
6. Web server configuration for HTTPS protocol
To ensure correct operation, it is necessary to use the HTTPS protocol. Using HTTP will lead to errors.
6.1 Generating self-signed SSL certificate
Install the SSL module for Apache2:
- shell
dnf install mod_ssl -y
Create a new directory to store the private key and certificate:
- shell
mkdir /etc/ssl/private
Generate a self-signed X.509 certificate for Apache2 using OpenSSL:
- shell
openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -subj '/CN=your.domain.name' -keyout /etc/ssl/private/apache-selfsigned.key -out /etc/ssl/certs/apache-selfsigned.crt
In the Common Name (CN) field, it is important to specify your server's IP address or hostname, as your certificate must match the domain (or IP address) of the website.
Generate Diffie-Hellman parameters with a key length of 2048:
- shell
openssl dhparam -out /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem 2048
Add Diffie-Hellman parameters to the self-signed certificate:
- shell
cat /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem | tee -a /etc/ssl/certs/apache-selfsigned.crt
Set root user permissions to protect the private key and certificate:
- shell
chmod 700 /etc/ssl/private
6.2 Virtual host configuration for HTTPS access
Before configuring the web server with SSL termination enabled, it is recommended to review the configuration features.
Open the configuration file to set up the HTTPS protocol:
- shell
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
Find the section starting with <VirtualHost _default_:443> and make the following changes:
- Uncomment the DocumentRoot line and change the path to the Passwork root directory
/var/www/public; - Uncomment the ServerName line and change
www.example.comto the server's IP address or domain (depending on the value specified in the certificate'sCommon Name):
- shell
DocumentRoot /var/www/public
ServerName passwork:443
- Add a
<Directory>directive afterServerName:
- shell
<Directory /var/www/public>
Options +FollowSymLinks -Indexes -MultiViews
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
- Update the paths to the certificate files generated earlier:
- shell
SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/apache-selfsigned.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/apache-selfsigned.key
- Change the .php file handler to proxy requests to the php-fpm socket:
- shell
<FilesMatch \.php$>
SetHandler "proxy:unix:/run/php-fpm/www.sock|fcgi://localhost/"
</FilesMatch>
- Verify that the
SSL Virtual Host Contextblock matches the example:
- shell
<VirtualHost _default_:443>
DocumentRoot "/var/www/public"
ServerName passwork:443
<Directory /var/www/public>
Options +FollowSymLinks -Indexes -MultiViews
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog logs/ssl_error_log
TransferLog logs/ssl_access_log
LogLevel warn
SSLEngine on
SSLHonorCipherOrder on
SSLCipherSuite PROFILE=SYSTEM
SSLProxyCipherSuite PROFILE=SYSTEM
SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/apache-selfsigned.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/apache-selfsigned.key
<FilesMatch \.php$>
SetHandler "proxy:unix:/run/php-fpm/www.sock|fcgi://localhost/"
</FilesMatch>
BrowserMatch "MSIE [2-5]" \
nokeepalive ssl-unclean-shutdown \
downgrade-1.0 force-response-1.0
CustomLog logs/ssl_request_log \
"%t %h %{SSL_PROTOCOL}x %{SSL_CIPHER}x \"%r\" %b"
</VirtualHost>
Important: copying and pasting the example above into the configuration file will cause errors because the example shows only a fragment of the block, not the full configuration file.
Restart services:
- shell
systemctl restart php-fpm
systemctl restart httpd
7. Completing checklist
When first connecting to Passwork, you need to complete a parameter checklist, during which the following will be performed:
- Checking necessary parameters
- Connecting to the MongoDB database
- Choosing a data encryption mode
- Randomly generated key for encrypting data in MongoDB
- License key verification
After completing the checklist, you will be prompted to create the first user in Passwork, where you need to specify a login, password, and email address for sending notifications.
Additional component parameters, security settings, and Passwork system configurations are available in the advanced settings section.

