Online installation
Minimum system requirements
Passwork is not demanding on system resources, and the required number of servers depends on the number of active users, the volume of stored data, and the system's fault tolerance requirements.
Please review the full system requirements.
If the server has 2-4 GB of RAM, we recommend enabling a SWAP file for proper compilation of all libraries.
System update
- DEB
- RPM
sudo apt-get update
sudo yum update
Installing Docker
- Download and install Docker version 18.06.0 or higher. Official installation guide.
- Install and enable Docker Compose. Official installation guide.
We recommend using Docker installed not via Snap.
Installing Passwork
To install Passwork, you need to obtain and run the script that will install the necessary components for the scripts to work.
Create a directory and navigate into it:
- shell
mkdir your_directory
cd your_directory
Copy the installation script:
- shell
wget https://repos.passwork.pro/repository/docker/passwork_compose_install.sh
Verifying authenticity of installation script
Check the hash of the passwork_compose_install.sh file to ensure its authenticity:
- shell
echo "84a13ba01703bfc2206e07491277f29d377ecc85e116be57d93be153593cd7ff passwork_compose_install.sh" | sha256sum --check
The system should output the message passwork_compose_install.sh: OK
Checking user permissions and running script
If the installation is not performed as root, ensure that the user is a member of the docker group.
You can check this as follows:
- shell
id $USER | grep docker
Add the user to the docker group like this:
- shell
sudo usermod -a -G docker $USER
Give the script execution permissions and run it:
- shell
chmod +x passwork_compose_install.sh
./passwork_compose_install.sh
The script uses apt or dnf, as well as curl. If your network uses a proxy server, you need to add environment variables:
export http_proxy=http://proxy.example.com:8080
export https_proxy=http://proxy.example.com:8080
Actions performed by the script
- Checking installed Docker
- Checking Docker version (above 18.06.0)
- Checking if Docker is running
- Checking user membership in the docker group or sudo rights
- Checking if the Docker Compose plugin is installed and enabled
- Checking if the system belongs to deb or rpm distribution
- Installing additional utilities for proper script operation:
curl,unzip, andjq - Requesting input of the Passwork client certificate
- Checking the certificate format compliance
- Validating the certificate
- Downloading and unpacking the archive with docker-compose build files
- Checking the environment variables file and adding the certificate number
- Running the Passwork code update script
- Verifying the archive with a digital signature
- Running
docker compose up -d
Installation script execution process
The script will check the current user's permissions and the versions of necessary components. In case of errors, the script will create a log in the format install_log_date.log and place the errors there:
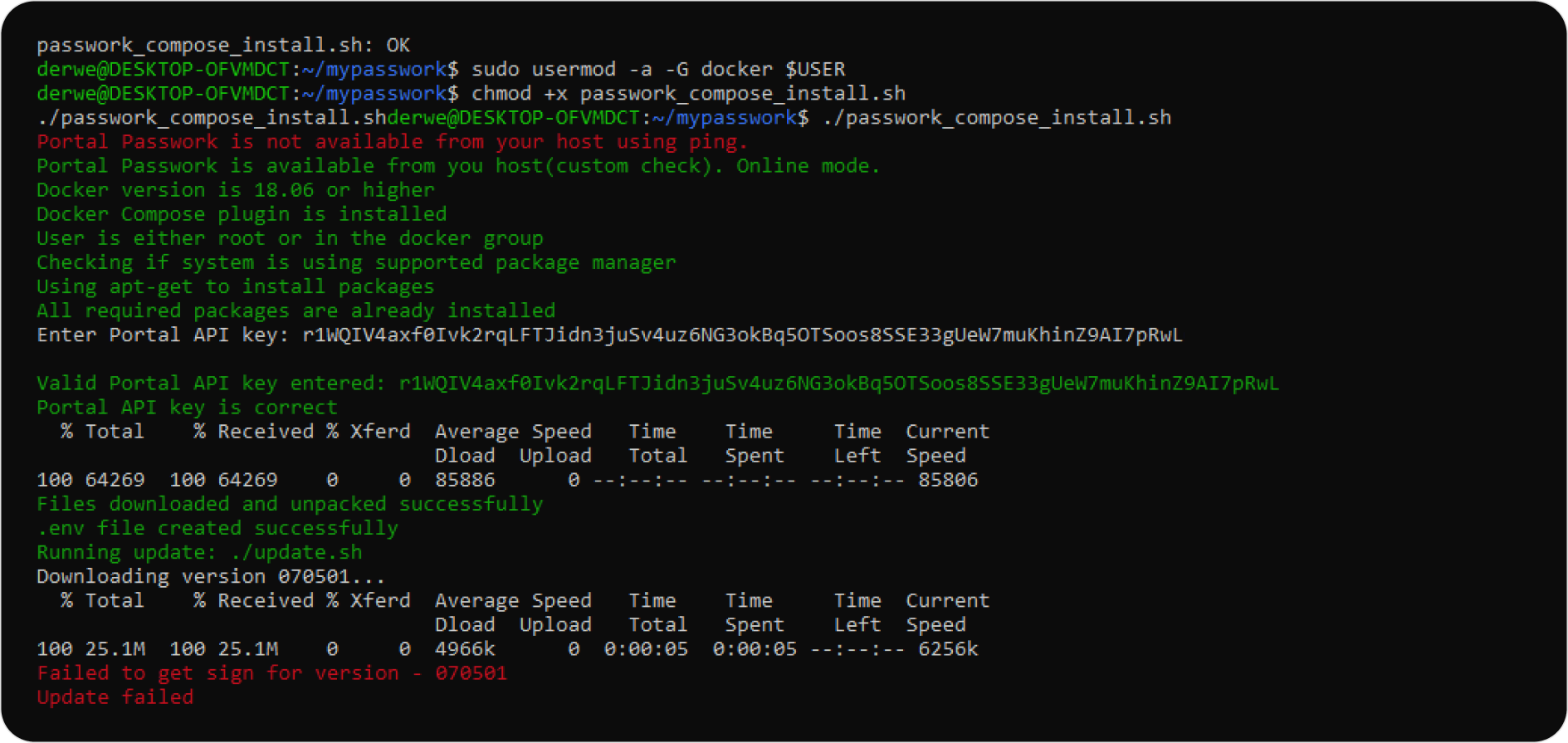
During execution, the script will request an API key from the Customer Portal:
After script completes
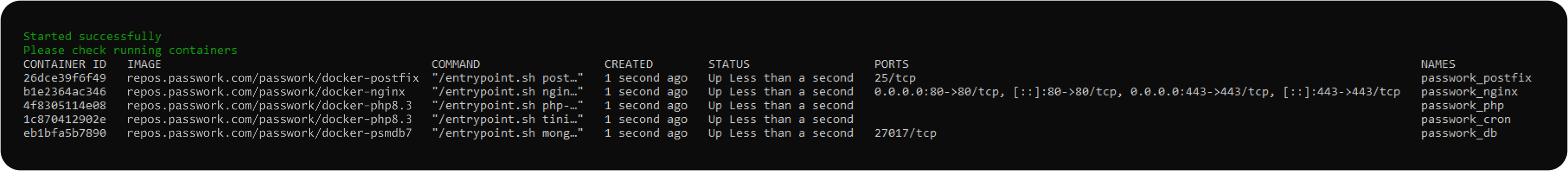
The script will automatically run docker ps. Please check the list of running containers. If containers were not started, check the installation result and log. Example of a correct result:
Before configuring the web server with SSL termination enabled, please review the configuration specifics.
Installation wizard
After building and starting the containers, Passwork will be available at the link https://your_servername.
By default, Passwork uses a self-signed certificate that is automatically generated during installation, so when you first open the page, you will see a message that the browser does not trust the site certificate.
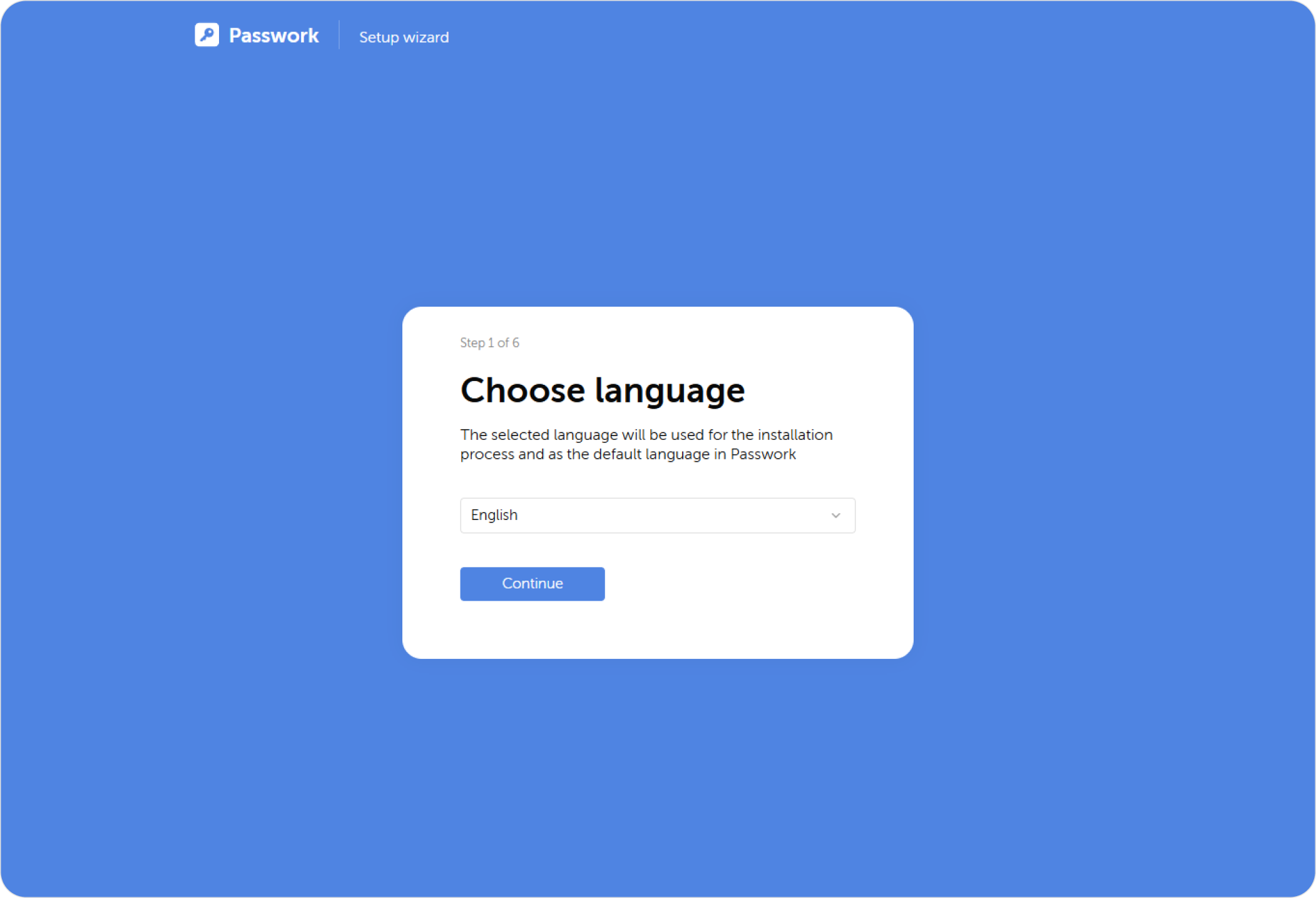
Choose language
At the first step, the system will prompt you to select the interface language:
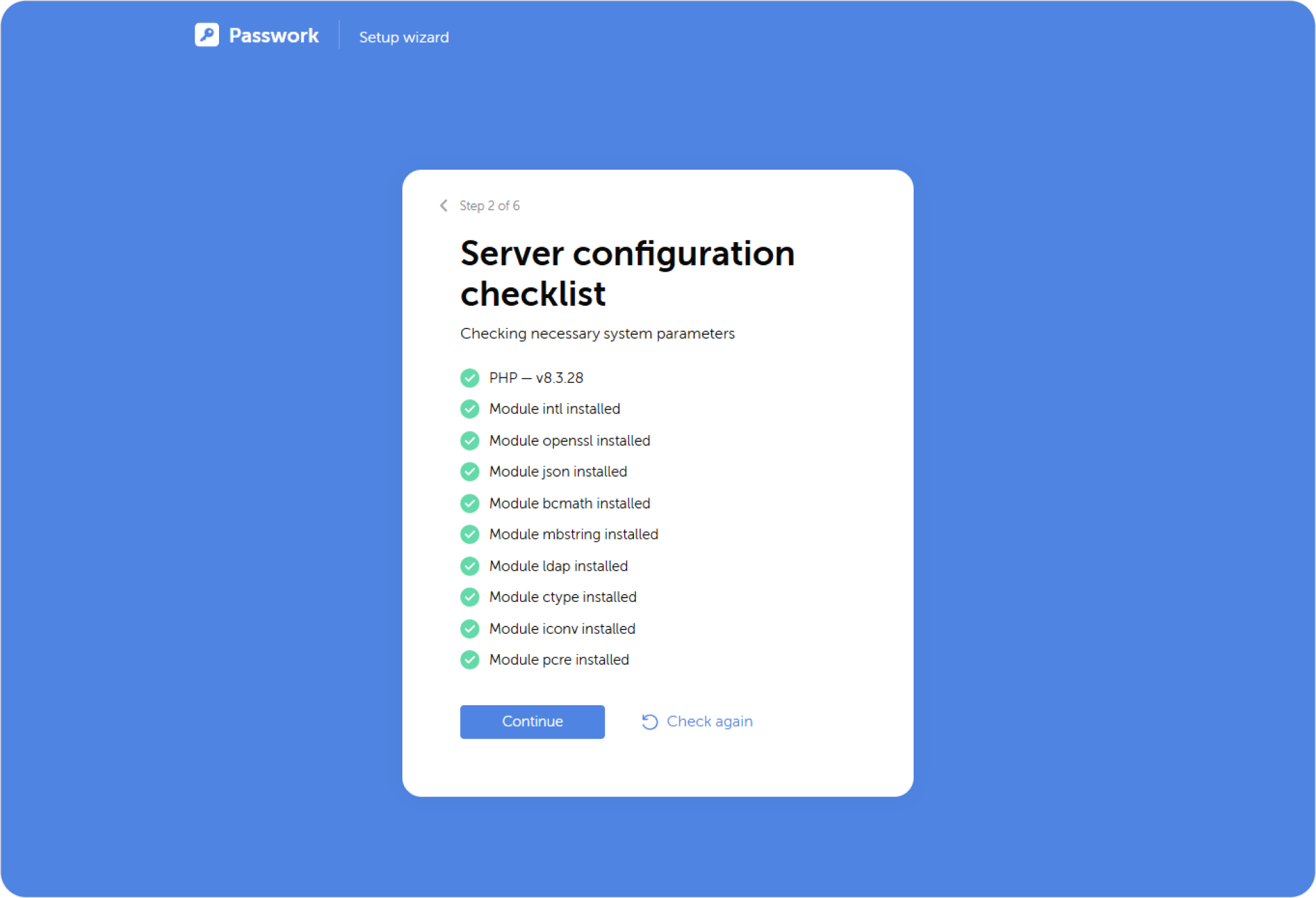
Server settings checklist
The checklist will show whether all components are installed on your server:
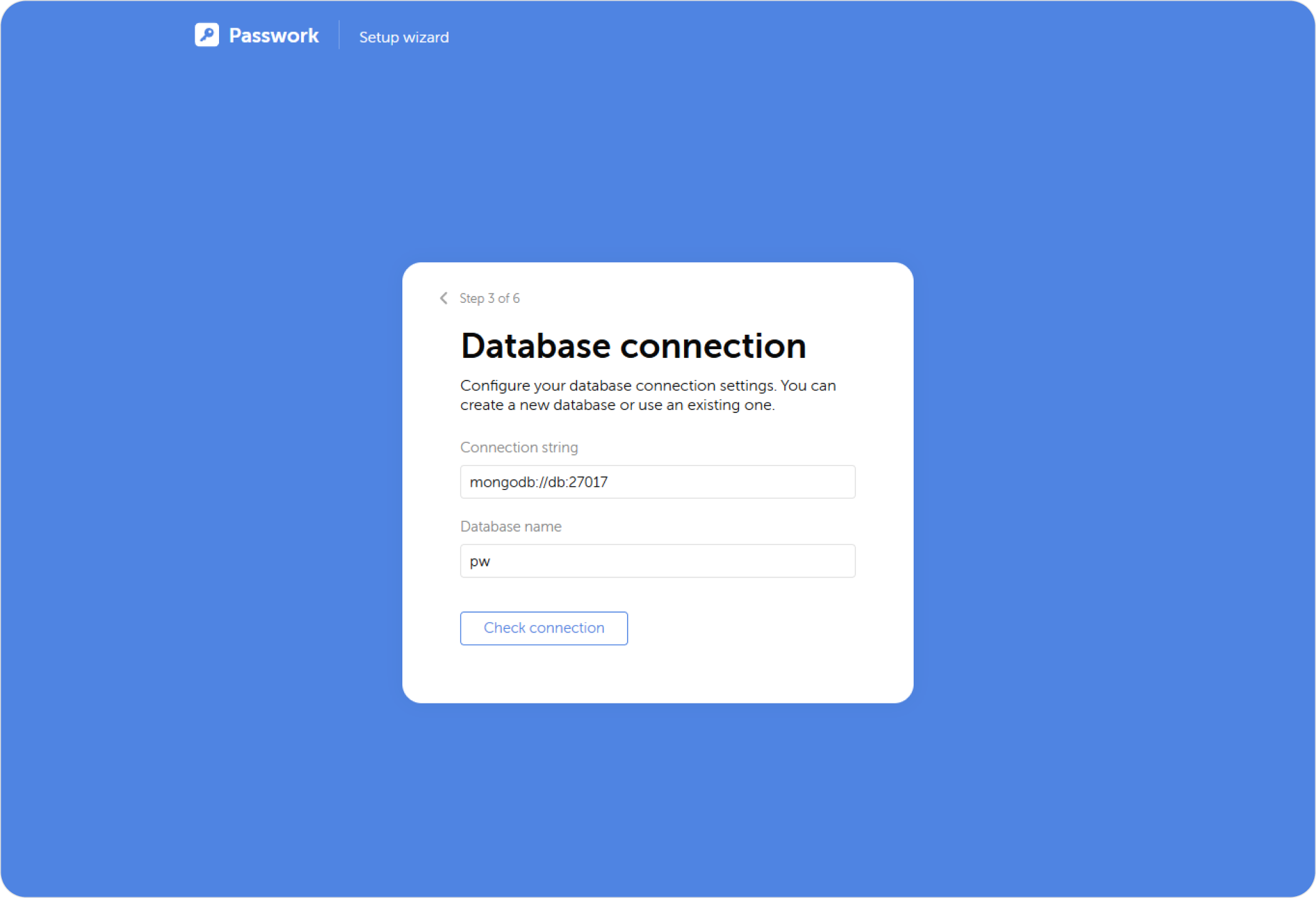
Connecting to database
Use the default MongoDB address for connection:
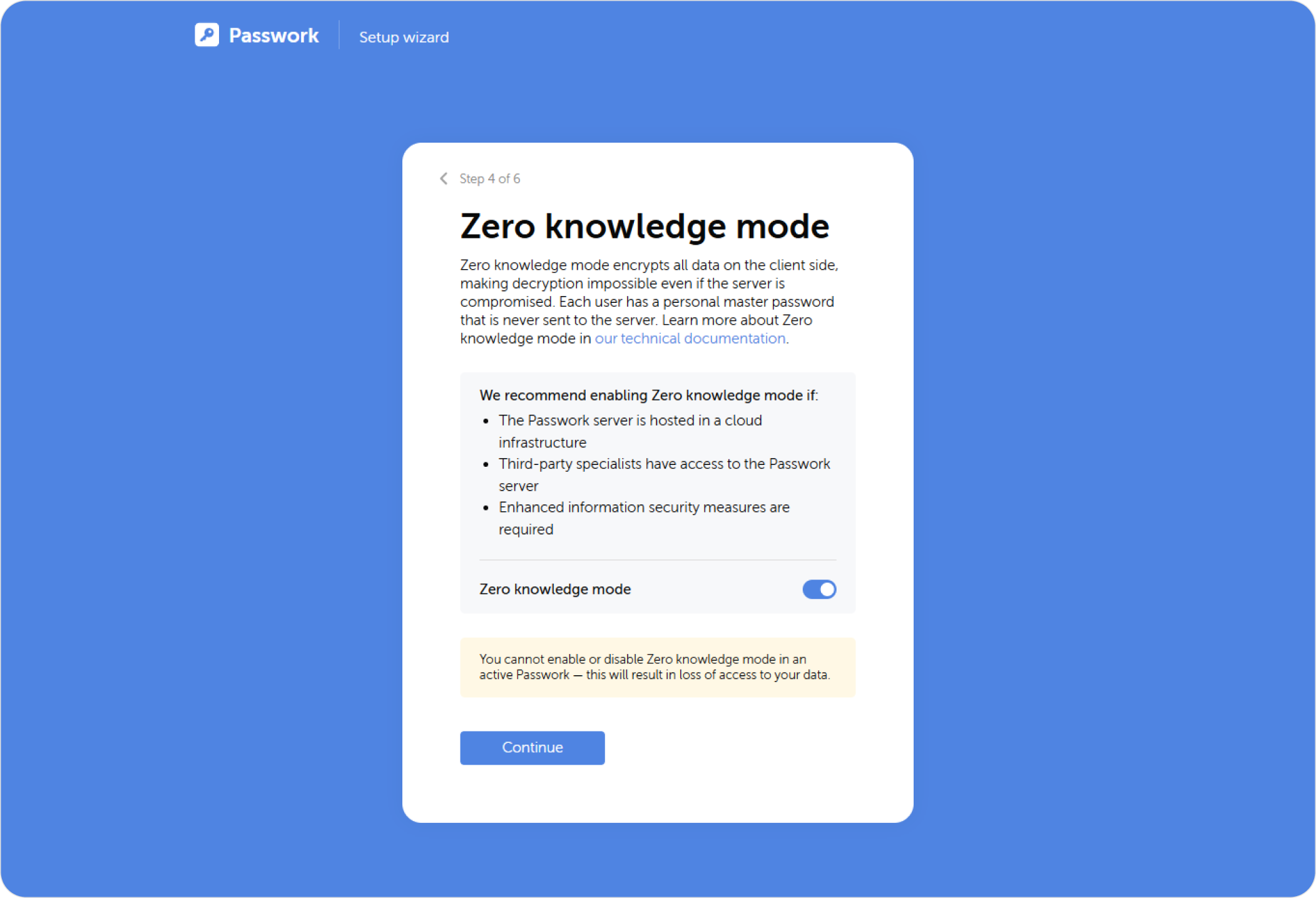
Zero knowledge mode
Client-side encryption adds a second layer of data protection and implements the Zero Knowledge model. This ensures maximum security when storing Passwork.
Client-side encryption mode is fundamental; it cannot be enabled or disabled in an already running Passwork (this will result in your inability to open data).
Learn more about how client-side encryption works — cryptography
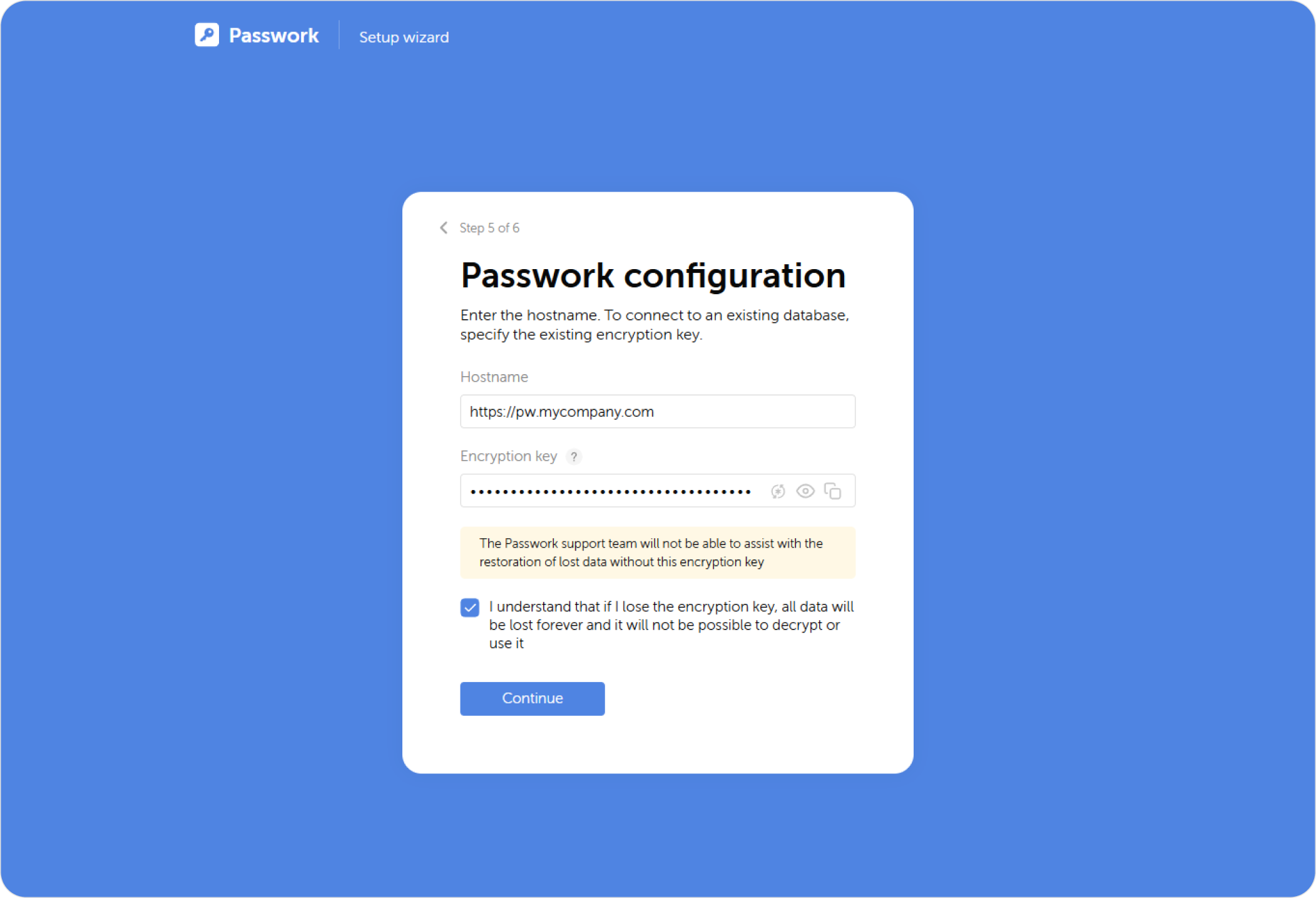
Passwork configuration
Passwork will generate a new key for server encryption. If you are connecting Passwork to an existing database, specify the existing encryption key:
Do not enter a key generated outside of Passwork. Using keys generated by third-party tools may cause errors.
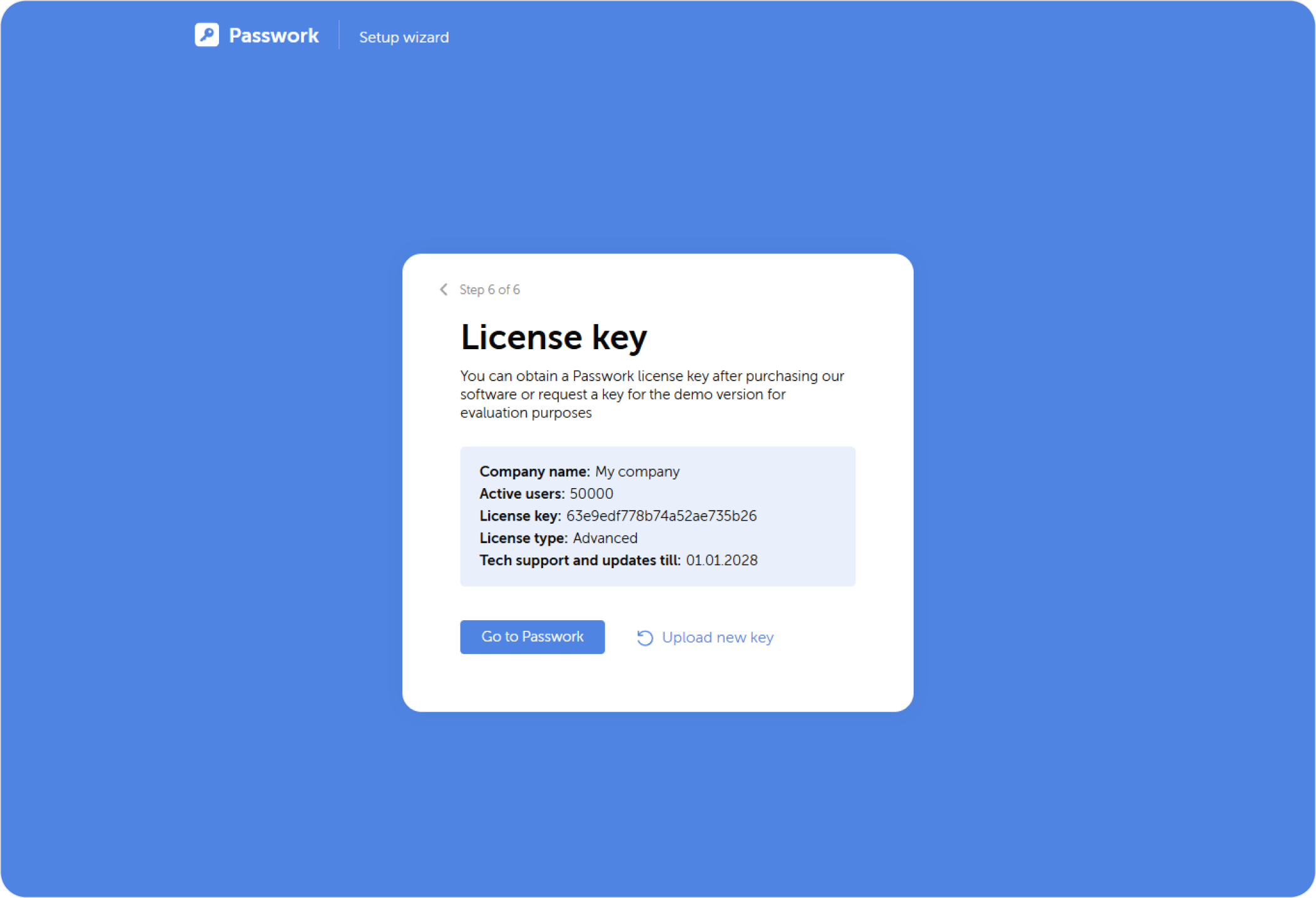
License key
License keys can be downloaded from your Passwork Customer Portal:
SSL certificate configuration
During installation, Passwork generates a self-signed certificate. Once installation is complete, you can use full SSL certificates.
Using your own certificate
- For certificates issued by a trusted issuer;
- For certificates issued by your organization's domain certification centers.
Rename and place your SSL certificate or certification chain in ./conf/ssl
- privkey.pem — private key
- fullchain.pem — certificate\certification chain
Using Let’s Encrypt
You can configure Let’s Encrypt if you do not have a domain certification center (a certificate issued by a trusted center) but have a public DNS name for your server.
Edit the .env file, changing and adding the following parameters:
USE_LETSENCRYPT=true
[email protected]
DOMAIN=example.com
COMPOSE_PROFILES="local_notify,mongo,certbot"
Save the changes and start the container:
- shell
docker compose up -d certbot
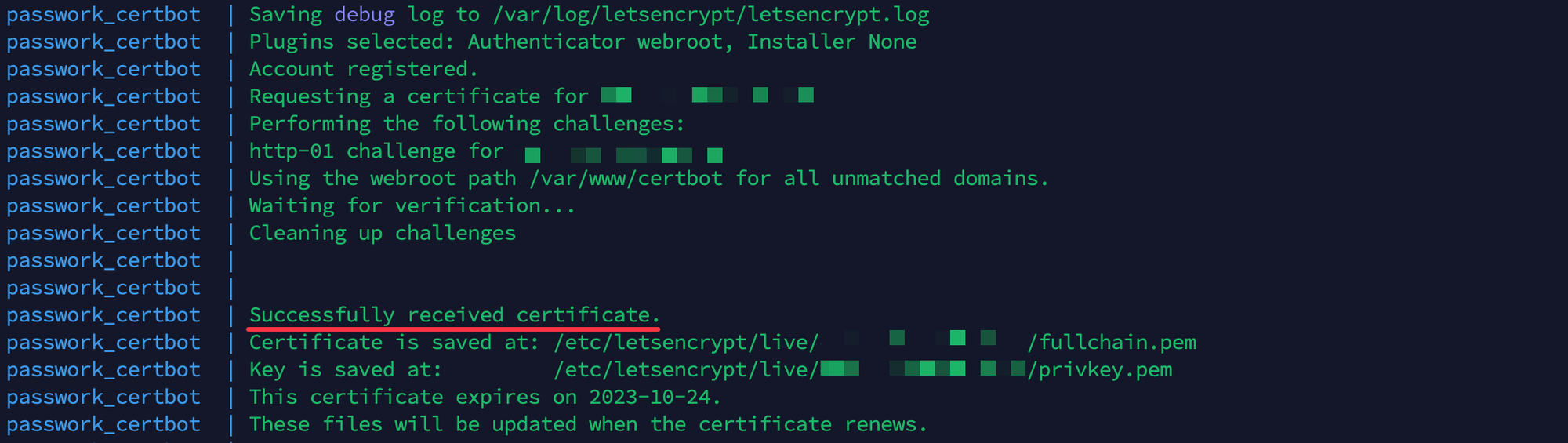
Check the container logs for certificate issuance:
- shell
docker compose logs certbot
Example of the certificate issuance process:
Recreate containers to update data using the new certificates:
- shell
docker compose up -d --force-recreate nginx certbot
As a result, Passwork will be available via HTTPS protocol using a certificate from Let’s Encrypt.

