
The International Space Station (ISS) represents one of humanity's greatest achievements in space exploration and scientific research. While its primary purpose is to facilitate scientific advancements and international cooperation, the ISS also plays a crucial role in advancing cybersecurity. In this article, we will explore the four main ways in which the ISS ensures cybersecurity and the unique challenges and opportunities it presents in the realm of securing information and communication in space.
Taking advantage of an isolated environment
The ISS operates in a unique environment that is isolated from the Earth's surface. This isolation offers inherent advantages for cybersecurity. Due to the absence of an atmosphere, the ISS is shielded from many terrestrial cybersecurity threats such as physical attacks or electromagnetic interference. This isolation enables the creation of a controlled and secure network environment, which is crucial for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and communication systems on board.
The isolation of the ISS from the Earth's surface provides a physical barrier against unauthorized access. The absence of a direct physical connection with Earth significantly reduces the risk of physical attacks, such as tampering with hardware or stealing sensitive information. This isolation also eliminates the risk of electromagnetic interference from Earth-based sources, which can disrupt communication systems and compromise data integrity. By leveraging this isolated environment, the ISS establishes a foundation for strong cybersecurity measures.
Developing a secure communication infrastructure
The ISS relies on a robust and secure communication infrastructure to establish connections with ground stations, enabling real-time communication between the astronauts and mission control. The communication channels are designed with strong encryption algorithms to protect sensitive information from interception and tampering. Secure protocols and authentication mechanisms ensure that only authorized personnel can access the systems and data on board the ISS. These measures prevent unauthorized access and help safeguard critical systems and scientific data from cyber threats.
The secure communication infrastructure on the ISS employs encryption algorithms, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), to protect the confidentiality of transmitted data. This ensures that any intercepted information remains unreadable and unusable to unauthorized individuals. Additionally, secure protocols like Secure Shell (SSH) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are used to establish encrypted connections between the ISS and ground stations, ensuring the integrity of data transmission. By implementing strong encryption and authentication mechanisms, the ISS establishes a secure communication framework that safeguards critical information from cyber attacks.
Fully-fledged redundancy and resilience
The ISS is equipped with redundant systems to ensure that even if one component fails, others can seamlessly take over, preventing disruptions to critical operations. Redundancy also extends to the communication infrastructure, with backup systems in place to ensure continuous connectivity. These redundancy measures help protect against cyber attacks and ensure the continued operation of vital systems, even in the face of potential threats.
The space environment poses various risks to hardware and software systems, including radiation, microgravity, and extreme temperatures. These factors increase the likelihood of system failures and can make the ISS vulnerable to cyber attacks. The ISS is designed to address this with redundant systems and backup mechanisms. If one component malfunctions or is compromised, alternative systems can take over seamlessly, maintaining the integrity of critical operations. This redundancy enhances the resilience of the ISS's cybersecurity infrastructure, minimizing the impact of cyber threats and ensuring the continuous functionality of essential systems.
Allowing international cooperation
The ISS is a prime example of international collaboration, with multiple nations working together toward common goals. This cooperation extends to cybersecurity efforts as well. Partner nations share their expertise and best practices to enhance the cybersecurity measures implemented on the ISS. Collaborative initiatives, such as information sharing and joint cybersecurity exercises, strengthen the collective ability to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber threats. By fostering international cooperation, the ISS contributes to the development of global cybersecurity standards and practices.
International cooperation in cybersecurity is crucial due to the interconnected nature of space missions and the shared responsibility of ensuring the security of the ISS. Partner nations exchange knowledge and expertise in areas such as threat intelligence, vulnerability assessments, and incident response to enhance the overall cybersecurity posture of the space station. By working together, nations can pool resources, share insights, and collectively address emerging cyber threats.
Furthermore, international cooperation enables the leveraging of diverse perspectives and experiences. Each partner nation brings its unique expertise and approaches to the table, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of cybersecurity challenges and solutions. This collaborative environment fosters innovation and enables the development of advanced technologies and strategies to mitigate cyber risks on the ISS.
Research and development
The ISS offers a unique environment for research and development in cybersecurity. Scientists and engineers can conduct experiments to better understand the effects of radiation, microgravity, and other space-related factors on hardware and software systems. This research helps in designing and implementing more resilient and secure technologies, not only for space missions but also for terrestrial applications. The knowledge gained from these experiments contributes to the advancement of cybersecurity practices, benefiting industries and governments worldwide.
The extreme conditions of space, such as radiation and microgravity, pose challenges to the durability and functionality of hardware and software systems. Conducting research on the ISS allows scientists to study the effects of these conditions on cybersecurity measures and develop innovative solutions. For example, experiments can be performed to test the resilience of encryption algorithms in the face of radiation-induced errors or to evaluate the performance of intrusion detection systems in a microgravity environment. The findings from these studies can be used to improve the design and implementation of cybersecurity technologies, making them more robust and effective in both space and terrestrial applications.
Moreover, the research and development conducted on the ISS can contribute to the advancement of cybersecurity knowledge in general. The unique experiments and studies conducted in the space environment provide insights and data that can enhance our understanding of cyber threats and vulnerabilities. This knowledge can be shared with the broader cybersecurity community, leading to the development of new techniques, tools, and best practices that can be applied to protect systems and data both in space and on Earth.
Conclusion
The International Space Station plays a vital role in advancing cybersecurity through its isolated environment, secure communication infrastructure, redundancy measures, international cooperation, and research opportunities. By leveraging these advantages, the ISS serves as a platform for innovation and collaboration, strengthening cybersecurity practices both in space and on Earth. As we continue to explore and expand our presence in space, the lessons learned from securing the ISS will undoubtedly shape the future of cybersecurity, ensuring the protection of critical systems and information in an increasingly interconnected world.
How the international space station ensures cybersecurity

The importance of healthcare data security solutions within the healthcare industry lies in safeguarding confidential patient information and ensuring compliance with regulations such as those outlined by HIPAA. In the past, protecting patient data was relatively straightforward, as it involved physical records stored in filing cabinets.
However, with the advent of technology and the digital era, patient records are now predominantly stored electronically on computers, servers, and storage devices. This shift brings heightened vulnerabilities to data breaches, malware, viruses, and other malicious attacks.
Contemporary healthcare professionals, including nurses, doctors, and other medical staff, heavily rely on technologies like computers and tablets to access, update, and record patient data. Furthermore, data sharing between multiple healthcare facilities and providers has become commonplace. Consequently, robust healthcare data security solutions become imperative to mitigate the risks associated with malicious data breaches and technical failures.
What is data security?
Data security refers to a range of precautionary measures implemented to safeguard and uphold the integrity of data. In the context of healthcare operations, the aim of data security is to establish a robust plan that maximizes the security of both general and patient data.
Healthcare institutions, such as Veterans Affairs (VA) hospitals, face heightened vulnerability to cyberattacks as hackers seek to obtain personal information for the purpose of committing medical fraud. It is crucial for healthcare organizations to meticulously assess potential causes of data breaches and devise comprehensive security solutions that address internal and external risk factors.
What are some factors that pose risks to healthcare data?
Healthcare organizations should be aware of various risk factors when developing data security solutions for their operations. These factors include, but are not limited to:
Utilization of outdated / legacy systems
Outdated operating systems, applications, and legacy systems create vulnerabilities that make it easier for hackers to access healthcare data. Since these systems are no longer supported by their creators, they lack proper security. Upgrading to newer and more secure systems is advisable.
Email scams with malware
Phishing scams have become increasingly sophisticated, often mimicking emails from familiar sources such as vendors or suppliers. Opening such emails or clicking on embedded links can result in malware installation, granting hackers access to healthcare data. It is crucial to educate employees about the importance of vigilance and avoiding suspicious emails.
Insufficient training in data security practices
When employees, contractors, vendors, and others lack proper training, they may unknowingly violate security protocols. It is vital to provide comprehensive training to all new staff members and regularly review and verify compliance with current data security practices among all employees.
Failure to maintain constant data security
Negligence in securing workstations is a common cause of data insecurity. Employees leaving workstations unlocked allows unauthorized individuals to access and steal data. Emphasizing the importance of locking workstations or enabling auto-locking features after brief periods of inactivity is crucial.
What factors contribute to the increased vulnerability of the healthcare sector to data breaches?
The healthcare industry faces a higher risk of data attacks compared to other sectors due to several key factors. Firstly, the nature of the data collected and stored by healthcare organizations is a significant factor. These organizations possess highly detailed patient records containing personal information such as names, dates of birth, addresses, social security numbers, and payment account details.
The extensive collection of such sensitive data in the healthcare sector inherently heightens the risk of data attacks. Moreover, healthcare data holds a greater value in illicit markets in comparison to other stolen data types. Consequently, it is of utmost importance for institutions like VA hospitals to implement robust data security solutions to mitigate these risks.
What types of security solutions should be employed for safeguarding healthcare data?
The choice of healthcare data security solutions depends on various factors such as data storage methods, the types of data collected, and the retention period. Generally, it is crucial to have comprehensive security measures in place that encompass protocols for patients, employees, contractors, vendors, and suppliers.
To ensure data protection, it is essential to tightly control data access permissions based on a need-to-know basis. For instance, patient insurance information and billing records should only be accessible to individuals responsible for processing insurance claims and managing patient balances.
Similarly, patient records containing diagnoses, treatment plans, and prescriptions should only be accessible to attending physicians, nurses, and other relevant healthcare professionals, with access granted on a case-by-case basis for specific data requirements.
Several common types of data security solutions can be implemented, including:
Data backup and recovery solutions
Regularly back-up data to secure servers, such as portable NAS servers, ensuring offsite storage for added security.
Data encryption
Employ encryption techniques when transferring data between workstations, servers, the internet, or cloud-based systems to ensure the highest level of protection.
Anti-virus / Malware / Spyware apps
Utilize appropriate applications to safeguard systems from viruses, malware, and spyware, and regularly update them.
System monitoring apps
Deploy monitoring applications to track file access, updates, creations, movements, and deletions, as well as to detect potential data breaches or unauthorized access and changes to user accounts.
Multi-factor authentication
Implement multi-factor authentication methods to enhance data security, requiring users to provide their username, password, and additional verification items like one-time passcodes sent to their email or mobile phones.
Ransomware protection
Employ specialized applications to protect workstations and servers from ransomware attacks, which can compromise data access and demand a ransom for restoration.
Employee training
Conduct regular training sessions with employees to ensure they are equipped with the necessary knowledge and precautions for safeguarding patient records, data, and confidential information.
It is important to note that the aforementioned list provides sample security solutions that can be employed to protect patient data, employee data, proprietary information, and other vital data within healthcare organizations.
Conclusion
The importance of healthcare data security solutions cannot be overstated within the healthcare sector. The shift from physical records to digital systems has introduced new vulnerabilities, necessitating the implementation of robust data security measures. Safeguarding confidential patient information and ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA is of utmost importance.
The healthcare industry faces various challenges to data security, including outdated systems, phishing scams, internal threats, weak wireless network security, inadequate password practices, lack of training, and insufficient maintenance of data security protocols. Addressing these challenges requires the adoption of suitable security solutions.
Effective security measures involve strict control of data access permissions, regular data backup and recovery, data encryption, utilization of anti-virus/malware/spyware applications, deployment of system monitoring tools, implementation of multi-factor authentication, adoption of ransomware protection mechanisms, and comprehensive employee training.
By embracing these measures, healthcare organizations can mitigate the risks associated with data breaches, protect patient data, and uphold the integrity of their operations. Prioritizing data security is crucial for establishing trust, preserving patient privacy, and upholding the highest standards of healthcare.
The significance of healthcare data security solutions

Wearable technology has become increasingly popular in recent years, with devices like the Apple Watch, Fitbit, and Xiaomi gaining significant market share. These devices offer a wide range of features, from tracking fitness goals to monitoring health data and staying connected with the digital world. However, with the rise of wearable tech, concerns have been raised about how secure these devices are and whether they put user data at risk.
Challenges
The types of data that wearable tech collects vary from device to device. Some devices, such as fitness trackers, collect basic health data such as heart rate and activity level. Other devices, such as smartwatches, can collect more sensitive data such as location, messages, and emails. This data is typically stored on the device and synced to the cloud, making it accessible from any device that the user is logged into.
One of the most significant concerns with wearable tech is the security of this data. If the device or cloud storage is not properly secured, the data could be accessed by hackers who could use it for malicious purposes. For example, hackers could use location data to track users' movements or steal their identity by accessing their personal information.
To protect user data, most wearable tech companies implement security measures. For example, the Apple Watch uses encryption to protect data stored on the device, and it requires a passcode or biometric authentication to access the device. Similarly, Fitbit and Xiaomi use encryption to protect user data and offer security features such as two-factor authentication.
Despite these measures, data breaches in wearable tech have unfortunately become more common in recent years, highlighting the need for continued vigilance when it comes to security measures. For example, in 2017, researchers discovered a vulnerability in the Bluetooth communication protocol used by many wearable devices. This vulnerability, known as BlueBorne, allowed hackers to take control of devices and steal sensitive data.
In 2019, it was discovered that several popular fitness apps had inadvertently exposed sensitive user data. The apps, which were used in conjunction with wearable fitness trackers, had failed to properly secure user data, leaving information like usernames, passwords, and exercise routines vulnerable to attack.
Another example of a wearable tech data breach occurred in 2018 when hackers stole sensitive data from the Polar fitness app. The data, which included location data, was collected by the app's users and stored on Polar's servers. However, the servers were not properly secured, allowing hackers to access the data and track the movements of military personnel and intelligence agents in sensitive locations.
How to protect your data and privacy?
To protect your data and privacy when using wearable tech, there are several steps you can take. Firstly, always use strong, unique passwords for your wearable tech accounts, and consider using a password manager to help generate and manage these passwords.
Secondly, ensure that your device's software is always up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. This will help to protect against known vulnerabilities and ensure that any new security features are in place.
Thirdly, be aware of the data that your wearable tech is collecting and where it is being stored. Check the privacy policy of your device and app to understand how your data is being used and shared. If you are concerned about your privacy, consider disabling certain features or opting out of data sharing.
Then, consider using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) to protect your online activities when using wearable tech. A VPN encrypts your internet connection, making it more difficult for hackers to intercept your data. VPNs are particularly useful when using public Wi-Fi, which is often unsecured and vulnerable to hacking.
Lastly, it's essential to know how to identify potential threats and scams that may target wearable tech users. This can include phishing emails or fake apps that may trick users into disclosing their personal information or installing malware on their devices.
Wearable tech in the workplace
Another important consideration when it comes to wearable tech security is the role of wearable tech in the workplace. Wearable tech is increasingly being used in workplace environments, where it can offer benefits like tracking employee productivity and health. However, it is essential to ensure that wearable tech devices used in the workplace are properly secured and that sensitive workplace data is not put at risk.
Organizations can take several steps to protect workplace data when using wearable tech.
Firstly, companies should develop a clear policy on the use of wearable tech in the workplace, outlining the acceptable use of these devices and the security measures that should be in place.
Secondly, companies should invest in secure wearable tech devices that offer robust security features, such as encryption and two-factor authentication. This will help to protect sensitive workplace data from unauthorized access and reduce the risk of data breaches.
Thirdly, organizations should provide training for employees on how to use wearable tech devices securely. This could include information on the importance of using strong passwords, keeping devices up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates, and being aware of potential security threats.
Finally, companies should implement monitoring and control measures to ensure that wearable tech devices used in the workplace are being used appropriately and that sensitive data is not being put at risk.
Conclusion
Overall, wearable tech devices offer many benefits for both individuals and organizations, but it is essential to take steps to protect data and privacy. By following the best practices outlined above, individuals and companies can minimize the risks associated with using wearable tech devices and enjoy the many benefits that these innovative devices offer.
How secure is wearable tech?

Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a technology that is used to control the use and distribution of digital content, including music, movies, e-books, and software. The primary purpose of DRM is to ensure that digital content is only used in ways that are authorized by the copyright owner. DRM technology works by placing restrictions on the use of digital content, which are then enforced through encryption, digital signatures, or other methods.
DRM systems typically involve the use of software that is integrated with the content. This software is designed to control how the content is used and to prevent unauthorized access to the content. DRM systems can also be integrated with hardware devices, such as DVD players or e-book readers, to ensure that the content is only used in authorized ways.
One of the most common methods of implementing DRM is through the use of encryption. When digital content is encrypted, it is transformed into a code that cannot be understood without a key. The key is typically stored on a server, and it is used to decrypt the content as and when it is needed. DRM systems can also use digital signatures to authenticate the content and to ensure that it has not been tampered with.
DRM systems are designed to be flexible so that they can be customized to meet the needs of different types of digital content and different types of users. For example, a DRM system for music may allow users to play the music on a limited number of devices, while a DRM system for software may allow users to install the software on a single device.
DRM technology is utilized to protect a wide range of digital content, including entertainment media such as books, music, and videos, as well as sensitive business data, database subscriptions, and software programs. DRM helps content creators and copyright holders control how their work is used and prevent unauthorized changes or misuse.
Here are some examples of DRM in action:
iTunes. Apple's iTunes store uses DRM to limit the number of devices customers can use to listen to songs. The audio files purchased from iTunes contain information about the purchase and usage of the songs, which prevents access from unauthorized devices. Additionally, the content in the iBooks store is protected by FairPlay technology, which ensures that books can only be read on iOS devices.
Digital Music. Spotify uses blockchain technology and DRM to identify songs played and pay the right artist through cryptocurrency. The music streaming company acquired Mediachain to assist in this process.
Microsoft Software. before downloading Microsoft software, such as Windows or Office, users must accept the company's user license and enter a key. Microsoft also uses a kind of DRM technology called PlayReady to secure the distribution of content over a network and prevent unauthorized use of its software.
Sensitive Documents. Many organizations use DRM to protect business-critical documents and sensitive information, such as confidential employee data, business plans, and contracts. DRM allows organizations to track who has viewed files, control access, and manage usage, as well as prevent alteration, duplication, saving, or printing.
Regulatory Compliance. DRM is important for organizations to comply with data protection regulations, such as HIPAA for healthcare organizations and CCPA and GDPR for all organizations.
Despite the benefits of DRM, there are also some criticisms of the technology. Some users argue that DRM restricts their ability to use digital content in ways that they feel are reasonable and legitimate. For example, they may feel that they should be able to transfer a purchased song from one device to another or to make a backup copy of a digital book.
Additionally, DRM systems can be vulnerable to hacking and other forms of attack. If a DRM system is compromised, it can allow unauthorized access to the content, which can undermine the purpose of the DRM system. This has led some users to view DRM as an unnecessary restriction on their ability to use digital content and as a threat to their privacy and security.
Another criticism of DRM is that it can make it difficult for users to access their digital content in the future. For example, if a user switches from one device to another, they may find that their DRM-protected content is not compatible with their new device. Additionally, if the company that provides the DRM system goes out of business or discontinues support for the system, users may be unable to access their content.
Despite these criticisms, DRM remains an important tool for protecting the rights of copyright owners and for ensuring that digital content is used in authorized ways. DRM systems have been used by a wide range of companies, including music labels, movie studios, and software publishers, to control the use and distribution of their digital content.
In recent years, some companies have started to move away from DRM, recognizing that it can be a barrier to the adoption of digital content. For example, some music labels have started to offer DRM-free music downloads, recognizing that users are more likely to purchase music if they are not restricted in their ability to use it. Additionally, some e-book publishers have started to offer DRM-free books, recognizing that users may be more likely to purchase books if they are not restricted in their ability to use them.
However, despite these trends, DRM remains an important tool for many companies, especially for those that want to ensure that their digital content is used in authorized ways. DRM is particularly important for companies that are concerned about piracy, as it can help to prevent unauthorized copying and distribution of their content.
In conclusion, DRM is a technology that is used to control the use and distribution of digital content. DRM systems work by placing restrictions on the use of digital content and enforcing these restrictions through encryption, digital signatures, or other methods.
While DRM has its benefits, including the protection of the rights of copyright owners, it also has its criticisms, including restrictions on the use of digital content and the potential for hacking and other forms of attack. Nevertheless, despite these criticisms, DRM remains an important tool for many companies and is likely to continue to be used in the future.
What is digital rights management (DRM) and how does it work

The importance of protecting the safety and security of our digital devices and the data stored on them has grown significantly as technology continues to advance and become more integrated into our everyday lives. The efficacy of antivirus software, as well as the role it plays in protecting users from online dangers, has come under close examination in recent years. This report goes into the present status of cybersecurity, the limitations and advantages of antivirus applications, and the alternative solutions that are available for defending your devices and data in 2023.
Understanding the modern cyber threat landscape
The landscape of cyber threats has expanded at an exponential rate over the past several years, with attacks becoming extremely advanced, diverse, and targeted. The term "cyber threats" no longer just refers just to viruses; they now include a wide variety of assaults, including the following:
Ransomware
A type of malware that encrypts a victim's files and demands a ransom in exchange for a decryption key.
Phishing attacks
Fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial data, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity.
Zero-day exploits
Attacks that take advantage of previously unknown vulnerabilities in software or hardware, giving developers no time to create and distribute patches.
Advanced persistent threats (APTs)
Long-term, targeted cyberattacks that often involve multiple attack vectors and are typically aimed at high-value targets, such as governments and large corporations.
Because cybercriminals are using more sophisticated strategies, it is essential for antivirus software and other cybersecurity solutions to evolve at the same rate in order to maintain their efficacy.
The limitations of traditional antivirus software
Traditional antivirus software primarily relies on signature-based detection, a method that compares files and programs against a database of known malware signatures. This strategy may be useful against recognized dangers, but it suffers from a number of limitations, including the:
Inability to detect new or unknown malware
Signature-based detection struggles to identify new malware variants or previously unknown threats, leaving users vulnerable to emerging cyber risks.
Slow response to new threats
Updating signature databases to include new malware often takes time, resulting in a window of vulnerability.
False positives and negatives
Signature-based detection can produce false positives (identifying benign files as malware) and false negatives (failing to detect actual malware), affecting the overall accuracy and effectiveness of the antivirus software.
The emergence of next-generation antivirus (NGAV) solutions
To address the limitations of traditional antivirus software and better combat the evolving threat landscape, the cybersecurity industry has developed next-generation antivirus solutions. NGAV products employ a combination of advanced techniques, such as:
Behavioral analytics
Monitoring the behavior of applications and processes to detect anomalies indicative of malicious activity, even if the malware itself is unknown or has no known signature.
Machine learning
Utilizing algorithms that learn from previous experiences to identify patterns and characteristics of malware, allowing for more accurate detection and classification.
Artificial intelligence
Incorporating AI to enhance threat detection capabilities and adapt to the ever-changing cyber threat landscape.
These advanced techniques make it possible for Next-Generation Antivirus (NGAV) solutions to offer protection that is more proactive and effective against new cyber threats.
Adopting a multi-layered security strategy
Although NGAV solutions represent a significant improvement over traditional antivirus programs, relying solely on a single security solution is insufficient. A multi-layered security approach, combining multiple tools and strategies, is essential for comprehensive protection in 2023. Key elements of a robust cybersecurity strategy include:
Regular software updates
Timely updates to your operating system and applications ensure that known vulnerabilities are patched, reducing opportunities for cybercriminals to exploit them.
A firewall
A strong firewall helps prevent unauthorized access to your network, serving as the first line of defense against potential intruders.
Security awareness training
Regular training and education for users about potential threats and best practices for online safety are crucial in preventing successful attacks, such as phishing and social engineering.
Data backup
Regularly backing up your data ensures that, in the event of a successful attack, you can recover quickly and minimize potential losses.
Endpoint detection and response (EDR)
EDR solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities, monitoring your devices and network for signs of compromise.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Network segmentation
Separating your network into smaller segments can help contain potential breaches and limit the spread of malware.
Vulnerability management
Regularly scanning your network and devices for vulnerabilities and addressing them promptly can significantly reduce your risk of cyberattacks.
Do you need antivirus software in 2023?
Given the complexities of the modern threat landscape, maintaining a robust cybersecurity posture is more critical than ever. Traditional antivirus software alone may not offer sufficient protection, but implementing next-generation antivirus solutions and adopting a multi-layered security approach can significantly enhance your defenses.
In conclusion, the question should not be whether you need antivirus software in 2023, but rather which solution best fits your needs and how it can be integrated into a comprehensive security strategy. By staying informed about emerging threats and continually adapting your defenses, you can reduce your risk of falling victim to cyberattacks and protect your valuable data and devices.
As a final note, it is crucial to remember that cybersecurity is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Depending on the nature of your online activities and the sensitivity of the data you handle, your security needs may differ. Regularly evaluating your cybersecurity measures and adapting them as needed will help ensure that you are adequately protected in the ever-evolving digital landscape of 2023.
Navigating the cybersecurity landscape in 2023: Do you need antivirus?

The vast majority of individuals look for nearby WiFi hotspots on their laptop computers. The most up-to-date personal computers have the ability to instantly recognize whether a wireless connection is present. But what if you don’t want to go through the effort of unpacking your laptop, starting it up, logging on, and then strolling about with it just to discover that there is no wireless network coverage in the area where you are? Because of this, having a WiFi sniffer on hand may be quite helpful in assisting you in rapidly locating the nearest WiFi network.
What is a WiFi sniffer?
A WiFi sniffer is a portable instrument that can locate the wifi network that is closest to the user. In addition to this, it will assist you in determining the strength of the WiFi signal, and if there are many signals, a WiFi sniffer will prioritize the signals in terms of their strength, which will save the user both time and annoyance.
WiFi sniffers are available in a variety of device formats, either as a stand-alone appliance or as software add-ons that interact with your wireless mobile device. You may get a WiFi sniffer in any of these two ways. The add-ons may often be obtained through the service provider of your mobile device, although standalone WiFi sniffers can be purchased at any store specializing in the sale of computers or electronic goods.
WiFi sniffers are able to handle all kinds of wireless network cards and come included with a Prism2 driver that may assist you in determining the intensity of the signal. WiFi sniffers are developed using C++ programming and operate using an "n-tier" structure. The gathering of data begins at the lowest tier and progresses up to the topmost layer, which is where the user interface is placed.
How does a WiFi sniffer work?
The operation of a WiFi sniffer does not call for a significant amount of technical expertise and may be carried out with relative ease. If you are using the standalone device, which is compact and portable, all you need to do is push and hold down the main button, aim it in any direction where you wish to locate a wireless network, and then use the gadget. This will activate the gadget, and while it is looking for a signal, the device will display lights that revolve in a circular pattern. The indicator light will remain constant after it finds a wireless signal. This means that it has detected a wireless network that is within a range of 300 feet of your device.
In the event that a signal cannot be found, the rotating lights will continue to do so, and it may be required to attempt to look in a different direction. If you are in an area where the wireless signal is poor, it is possible that it may be necessary to make adjustments to the antenna. WiFi sniffers that are add-ons to your mobile device do their functions in a manner that is analogous to that of the standalone device. Nonetheless, their specific capabilities change depending on the sort of mobile device that you are utilizing.
WiFi sniffer features
Just like there are many various brands of wireless devices available on the market, there are also many different brands of WiFi sniffers, each of which has functions that vary depending on the model of the device. While searching for a high-quality WiFi sniffer, one of the qualities you should look for is a device that is capable of avoiding interference from other electronic gadgets and appliances, such as mobile phones, Bluetooth devices, and microwave ovens. The better-grade devices will have the ability to capture a wireless signal regardless of the environment that they are placed in.
The most effective kind of WiFi sniffer often operates on the 2.4GHz frequency band and has the capacity to identify WiFi signals for both 802.11b and 802.11b/g. It needs to be easy to carry around with you, be convenient, and be small enough to fit in your pocket or laptop bag.
WiFi sniffers that have the qualities described above are also useful tools for usage in the house. Whether you are setting up a home office or Internet-ready gadgets, a WiFi sniffer can assist you in determining the areas of your home with the strongest wireless signal so that you can optimize the signal's capabilities and get the most out of your home office or devices.
Isn’t a WiFi sniffer illegal?
No. Stumbling across a wireless network by using a WiFi sniffer is a much simpler process than wireless sniffing, as the two terms refer to quite distinct activities. A WiFi sniffer's sole purpose is to discover the location of the nearest accessible wireless connection; however, it cannot actually join the network itself. Eavesdropping on conversations taking place inside of wireless networks is what's known as wireless sniffing, and it's a technique that's intended to break into a network. The former is permitted but the latter is not, particularly when it is utilized in the commission of illegal conduct.
On the other hand, wireless sniffing is entirely within the law when it is employed by IT employees to monitor network incursions on a business or government infrastructure. This is the case whether the infrastructure is owned by a private company or the government. Monitoring the information packets that are sent over a network is what's referred to as "intrusion detection," and it's used to protect sensitive data from being stolen by hackers and other malicious users of the internet.
There are a few businesses that have made it illegal for customers to use WiFi sniffers, which are devices that randomly search for available wifi networks. Instead, corporations are deploying apps that are based on directories and that can be allowed for usage by mobile employees as well as other people.
Hopefully, the material presented here will assist you in gaining a deeper comprehension of WiFi sniffers and the functions they perform. In short, they’ll help you save time and stress while maximizing the signal strength of your home wireless network.
How WiFi sniffers work?

The majority of individuals don’t put much thought into the kind of web browser that they use. Typically, laptops or smartphones are equipped with a default browser like Microsoft Edge or Safari, leading people to assume it's the finest or sole choice available. Nevertheless, there are several other browser options to select from.
Your web browser is the medium through which you communicate with the majority of the internet, resulting in a substantial amount of personal information being managed by it. It is essential to ensure that you are using a secure browser since this data is highly valuable.
So, how much is your data worth? To marketing firms — quite a bit. Companies can sell your browsing data to third parties for profit, and that's just the start of it. Hackers are always on the lookout for people who are not using a secure browser, and exposing personal data in this manner can be incredibly risky.
Your browser and its ability to protect your privacy and security are critical. As a result, let's go through the top five secure browsers for 2023.
Firefox

In 2023, Firefox is considered one of the best web browsers as it is secure, open-source, and offers numerous customization options. Its high level of customization makes it an excellent choice for advanced users, yet it is also user-friendly, making it a great option for non-tech-savvy users.
Firefox blocks third-party tracking cookies automatically, resulting in faster browsing speeds than other browsers that allow websites to track user activity, like Chrome. It also features various security measures, such as anti-phishing and malware protection, minimal data collection, automatic tracker blocking, and encrypted browsing with DNS over HTTPS (DoH). It is also compatible with third-party security extensions.
Firefox's anti-phishing protections are impressive, as it is highly effective in detecting risky and known phishing sites when tested against a database of such sites. Additionally, Firefox's DoH protections encrypt search queries with CloudFlare or NextDNS's encrypted DNS servers, making it challenging for third parties to steal browsing history.
Although many highly secure browsers compromise convenience for protection, Firefox is simple to use and provides advanced security features. Users can adjust security settings, anti-tracker settings, and anti-phishing protections according to their preferences. Firefox is compatible with Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS.
Tor Browser

In terms of user privacy, Tor Browser is the top choice; however, it is not as fast as most of its competitors.
The name "Tor" is derived from "The Onion Routing," a technology that hides the user's IP address by encrypting web traffic and routing it through multiple servers. As a result, before a user's computer can access a website, their traffic must first pass through Tor's secure server network. Tor has been shown to conceal user activity from ISPs, hackers, trackers, and even governments. The NSA was reportedly unable to hack into the Tor network, as stated in Edward Snowden's leaked documents. Tor Browser is banned in certain countries that censor the internet because it provides users with unrestricted access to the web.
Tor's data collection policy is minimally intrusive, as it only collects usage data to assess browser performance. Despite being an advanced browser, Tor Browser's interface is user-friendly, and it uses the same source code as Firefox, with minor variations. Users can even install most Firefox extensions into Tor Browser. However, browser extensions increase the likelihood of machine identification by network surveillance tools, so users who wish to remain as private as possible should avoid using them.
While Tor Browser is highly secure, its onion routing technology will slow down the internet connection, similar to the effect of using a VPN. When users' traffic bounces off multiple servers, their connection speed is adversely affected. Nonetheless, Tor may be the ideal choice for users with a reliable internet connection who is willing to trade some speed for high security. Tor Browser is compatible with Windows, Android, macOS, and Linux.
Brave

Brave is a web browser that offers a fast browsing experience and comes with built-in ad and tracker-blocking features. With its "Shields" feature, Brave can automatically block ads and trackers, which allows it to load websites much faster than other browsers. This feature also provides an added layer of protection by blocking malicious web scripts that may try to infiltrate your device. In addition, Brave automatically sets up HTTPS connections, which use a secure encryption protocol to protect user traffic.
One of Brave's standout features is its ability to use Tor technology in Private Browsing mode, which encrypts your traffic through the Tor network. This ensures that your browsing activity remains hidden not only from other users on your device but also from your ISP and other network spies.
Brave also has a unique ad-buying program called Brave Rewards, which allows users to earn BAT (a type of cryptocurrency) by viewing or clicking on sponsored ads. These BATs can then be transferred to the sites and content creators of your choice. This program offers a great revenue solution for content creators as Brave ads generate revenue without using trackers, selling user data, or pop-ups that interrupt the browsing experience. Brave is available for Windows, Android, iOS, macOS, and Linux.
Google Chrome

The reason why Google Chrome is the most popular browser in the world is that it is compatible with all major platforms and provides users with an excellent interface as well as thousands of useful extensions. Google, with its large number of staff and resources, constantly updates and patches Chrome more quickly than any other browser developer to patch network vulnerabilities, man-in-the-middle attacks, browser glitches, and exploitable security holes.
Chrome's Safe Browsing feature uses Google's extensive database of unsafe sites to flag suspicious web pages, which is updated daily and detects more phishing sites than most other browsers. Additionally, Chrome uses sandboxing to prevent malicious web scripts and invasive trackers from stealing data or hacking devices. Users can choose DNS over HTTPS (DoH) protection in Chrome's settings for added privacy and protection from ISPs, governments, and network-snooping hackers, which is turned on by default in Firefox but only requires a single click in Chrome.
It's important to mention that Chrome's tracker blocking is limited due to Google's reliance on web trackers to gather user data for advertisers. Chrome collects user data by default, and while much of this data is used to enhance Chrome's security, it's also shared within the entire Google ecosystem, including advertisers and potentially even governments. Despite this, Chrome has many trackers and ad-blocking plugins available for security-oriented users, such as Avira Safe Shopping. Although Chrome may be one of the most secure browsers, it's also one of the worst for user privacy. Google Chrome is available for Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Linux.
Microsoft Edge

Microsoft Edge is a vast improvement compared to its predecessor, Internet Explorer. Edge is a user-friendly, Chromium-based browser that boasts robust security tools, including Edge SmartScreen anti-phishing technology, which detects phishing sites more effectively than Chrome in tests.
In addition to its security features, Edge also offers a simple tracker-blocking system that has three levels: Basic, Balanced, and Strict. The Strict setting blocks most trackers and cookies, including those necessary for some sites to function. In contrast, the Balanced setting performed best in tests, detecting and blocking the most invasive cookies. This makes it much easier to manage online privacy than in Chrome, where the options are limited to
"Allow All," "Block Third-Party," and "Block All."
Like Chrome and Firefox, Edge now supports DNS over HTTPS by default, which enhances user privacy when browsing the web. Microsoft Edge is available for Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS.
Conclusion
It can be difficult to determine whether a browser is truly secure or not, but the browsers mentioned in this article offer a good level of privacy. While this is a great start, for the most secure browsing experience, I suggest using a combination of a secure browser and a virtual private network (VPN). A VPN adds an extra layer of protection to your online activity by encrypting your entire Internet connection, making it much more difficult for anyone to intercept your data or monitor your browsing habits.
By using a quality VPN, you can also hide your real location and appear to be browsing from a different location altogether. This can be especially useful for accessing content that may be restricted in your country or region. With a secure browser and a VPN, you can enjoy a more private and secure browsing experience, free from the prying eyes of hackers, governments, and other third parties that may be trying to track your online activity.
Best safety browsers in 2023

In an era where cybercrime is rampant, businesses must take a proactive approach to safeguard their confidential information. In 2021 alone, over 118 million people have been affected by data breaches, and this number is expected to rise exponentially.
In this post, we’ll discuss some of the best practices for businesses to protect themselves from cyber threats.
Always have a back-up
A good backup system is one of the best ways to maintain computers’ security and protect your business’s data. Regularly backing up important files can help ensure that you don’t lose any information if a cyber incident or computer issue occurs. Here are some tips on how to effectively back up your data:
- Use multiple backup methods. Have an effective backup system by using daily incremental backups to portable devices or cloud storage, end-of-week server backups, quarterly server backups, and yearly server backups. Remember to regularly check and test whether you can restore your data from these backups.
- Use portable devices. Consider using external drives or portable devices such as USB sticks to store your data. Store the devices separately offsite, and make sure they are not connected to the computer when not in use to prevent malicious attacks.
- Utilize cloud storage solutions. Cloud storage solutions are a great way of backing up all your important information. Choose a solution that provides encryption for transferring and storing your data and multi-factor authentication for access.
- Practice safe backup habits. Make it a habit to regularly back up your data, not just once but multiple times throughout the week or month, depending on the type of information you’re backing up. Additionally, it’s important to practice safe backup habits, such as keeping your devices away from computers when not in use and regularly testing that your data is properly backed up.
Train your employees
To protect your business from cyber threats, educating your employees about the risks and how to stay safe is essential. Training should focus on identifying phishing emails, using strong passwords, and reporting any suspicious activity immediately to the IT department.
Ensure that everyone is up-to-date with the latest threats and strategies for protection by conducting regular cybersecurity training sessions with all of your employees. Provide helpful resources such as tips for creating secure passwords, methods for spotting phishing attempts, and steps for safely sharing confidential information online.
Putting this emphasis on education and training will help create an environment of alertness so that any potential risk can be identified quickly and addressed appropriately.
Password management
Weak passwords are one of the most common entry points for cyber attackers, so using a secure password and password manager is essential to keep your business safe.
A password manager is a tool that allows you to store and manage all your passwords securely, with only one strong master password needed to access them all. Here are some tips for creating strong passwords and using a reliable password manager:
- Create strong passwords. Choose passwords that include numbers, symbols, upper-case letters, and lower-case letters. Avoid using personal information like birthdays or pet names in your passwords. Additionally, avoid using the same username/password combination for multiple accounts.
- Use a password manager. A reliable password manager will help you create and store secure passwords. Be sure to select a trustworthy provider, as they will be responsible for protecting your data.
An on-premise password manager like Passwork is an excellent option for businesses that need to store passwords on their own servers. Passwork provides the advantage of having full control over your data and features like password sharing and a secure audit log.
- Enable multi-factor authentication. Adding an extra layer of security to your accounts is easy with multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA requires two or more pieces of evidence to authenticate the user's identity, such as passwords and biometric data. Most password managers can enable MFA for all your accounts, so be sure to take advantage of this feature.
Finally, make sure you update your passwords regularly and always keep them private. Following these tips will help ensure that you are protecting your business from cyber threats.
Securing your network
Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) effectively protects your business's sensitive data and prevents unauthorized access to your network. A VPN creates an encrypted connection between your device and the internet, making it more difficult for hackers or malicious actors to intercept and access confidential information. Here are some tips on how to leverage a VPN for optimal security:
- Research the best VPN providers for features that best suit the needs of your organization
- Ensure that the provider meets industry standards such as AES 256-bit encryption
- Set up two-factor authentication with users’ login credentials
- Configure the VPN for reliable and secure connections
- Monitor your network for any suspicious activity or unauthorized access attempts
- Make sure to update the VPN software with new security patches regularly
- Train users on the proper internet safety and best practices when using a VPN
- Use an antivirus program and scan all devices connected to the network for malware threats
VPNs are not only important for protecting data and preventing unauthorized access but also for maintaining user privacy. By encrypting the data sent and received over the internet, your organization can ensure that any information stays secure and confidential.
Consistent vulnerability assessments are crucial
Organizations of all sizes must remain vigilant in mitigating cyber threats — and one of the best ways to do this is by conducting regular vulnerability assessments. This will help identify any potential weaknesses or vulnerabilities that could be used by malicious actors to gain access to your system, allowing you to patch and address them before they become a problem.
Here are a few steps to help get you started:
Develop an assessment plan for your organization
Before starting, it’s important to understand the scope and objectives of the vulnerability assessment. Define the overall goals and objectives before identifying any assets or systems that should be included in the assessment.
Identify and document threats
Once you have developed a plan, it’s time to begin searching for potential vulnerabilities within your system. You can use various open-source intelligence techniques, such as scanning public databases and researching known security issues with similar software versions or operating systems that are present in your system.
Create a testing environment
After potential threats have been identified and documented, you should create a safe testing environment to validate the vulnerability assessment results. Doing so will help ensure that any tests conducted do not adversely affect production systems.
Run automated scans
Following the creation of your secure test environment, it’s time to run automated scans on your organization's target systems or assets. This should include both internal and external scanning tools, such as port scanners, web application scanners, or configuration management tools, depending on the scope of the assessment.
Analyze scan results
Once the automated scans have been completed, it’s time to analyze the results and identify any potential issues or vulnerabilities. Assess any weaknesses present in order to prioritize and address them more effectively.
Develop a remediation plan
After identifying potential security issues, you should develop a remediation plan based on the risk level of each issue. This could include patching vulnerable systems, implementing new security measures, or restricting access to certain areas of your system, depending on the severity of the threat.
By conducting regular vulnerability assessments, organizations can stay ahead of cyber threats and ensure their systems remain secure.
Bottom line
Protecting your business from cyber threats should be a top priority for any organization. With the increasing prevalence of cybercrime and data breaches, implementing effective cybersecurity practices is more important than ever.
By regularly backing up important files, training employees on identifying and reporting potential threats, using a secure password manager, utilizing a VPN, and conducting consistent vulnerability assessments, businesses can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to cyber-attacks.
5 ways to keep your business safe from cyber threats

In recent years, the issue of user privacy has become more critical than ever before. With the rise of social media and other online platforms, companies are collecting vast amounts of user data, which can be used for various purposes. While some of these purposes may be benign, such as improving the user experience or providing targeted advertising, others may be more nefarious, such as selling user data to third parties or engaging in targeted surveillance.
There are now many apps that are activated by code words — they are called " marker words". These words can activate the listening function on your gadget covertly and completely invisibly. It can be not only "OK, Google" or "Hi, Siri", but also other completely unrelated words or sounds.
Perhaps you may have noticed Instagram advertising something you recently talked to your friends about even in real-time without holding your phone. If so, you know you're being bugged.
So, who's eavesdropping on us?

Facebook reportedly hired hundreds of third-party contractors to transcribe voice messages but stopped the practice in July 2019 after it was made public. The contractors were not always clear on why they were listening to certain conversations and did not understand how the messages were obtained. Facebook did not inform its users about this development, which involved the potential listening of personal voicemails by unauthorized individuals.
Microsoft

Microsoft's employees were reported to have listened to personal audio recordings made through Cortana and Skype Translator services. However, Microsoft did not deny this claim and instead included the information in the company's privacy policy. Microsoft believes in maintaining an honest relationship with its users and believes they have the right to know that their conversations may be overheard. Nonetheless, Microsoft did not previously disclose this information to its users, and it is possible that the company decided to proactively share the information as they had been listening to audio recordings for some time. This is in contrast to other companies that faced privacy violations but did not disclose their actions to their users.
Apple

It has been reported that contractors who test Apple's Siri voice assistant for accuracy may be listening in on users' private conversations. It should be noted that Siri can be activated by more than just the phrase "Hey, Siri" and can be triggered by similar-sounding words, background noise, or hand movements. This has resulted in Siri being inadvertently activated during private conversations, leading to the collection of personal information and recordings of private conversations, including those between doctors during commercial transactions. These recordings are often accompanied by data that can reveal the location or personal contacts of the users. Apple representatives claim to be working to address these concerns in order to protect users' personal information.
Amazon

Over one thousand Amazon contractors are listening to voice recordings made in the homes and offices of Echo voice assistant owners. These contractors are required to sign non-disclosure agreements and are not allowed to discuss the program publicly. They work nine-hour shifts and analyze up to 1,000 sound recordings per shift, but even if they have concerns about what they hear, they are required to adhere to the non-disclosure policy. Amazon claims to take the security and privacy of its customer's personal information seriously, and employees do not have access to information that could identify a person or account directly. It is important to note that users can disable the use of their personal voice records for the development of new features in Amazon's Alexa privacy settings.

Google employs experts to listen to the voice commands given by users to its voice assistant. These recordings are made after the voice assistant has heard the phrase "Ok, Google" and can be made on smartphones using Google Assistant or on the Google Home smart speaker. Google shares snippets of these recordings between users and linguists around the world to improve the voice assistant, but claims to have access to no more than 0.2% of all user commands. The company has prohibited employees from transcribing conversations or other extraneous sounds. However, in June 2019, it was reported that a significant leak of audio recordings of users occurred, with over a thousand recordings, including personal conversations between parents and children, addresses, and work calls being exposed. Some recordings were made accidentally due to the assistant being activated by mistake. Google attributed the leak to the actions of one linguist and claimed to be investigating the matter.
Conclusion
Despite the concerns that these data collection practices raise, companies often argue that they are necessary to improve user experience and provide more personalized services.
However, many users remain skeptical of these claims and are increasingly concerned about the potential for abuse. For example, data breaches can expose user data to hackers and other malicious actors, potentially putting users at risk of identity theft and other forms of cybercrime. Additionally, governments and other organizations may use user data to engage in targeted surveillance, raising concerns about civil liberties and individual privacy.
In response to these concerns, governments and regulatory bodies have taken steps to regulate the collection and use of user data. In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR) have strengthened data privacy laws and given users greater control over their data. In the United States, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) has similarly sought to protect user privacy by requiring companies to disclose what data they collect and allowing users to opt out of data sharing.
Despite these efforts, however, the issue of user privacy remains a contentious one. As technology continues to advance, companies will undoubtedly find new ways to collect and utilize user data, raising new concerns about privacy and security. It is therefore crucial that users remain vigilant and informed about the data collection practices of companies they interact with, and for governments and regulatory bodies to continue to monitor and regulate these practices to protect user privacy.
Are companies spying on their users in 2023?

People frequently utilize various VPN servers at work. Off-the-shelf options are good, but we've come to learn that a personal VPN offers substantial benefits. To appreciate the benefits of creating your own VPN server over purchasing one, consider why VPNs are used in the first place:
• To prevent others from intercepting your lines of communication
• To circumvent access limitations to a specific resource in your own nation or a foreign one
• Conceal personal information from the Internet provider (the owner of the WI-FI access point)
• Leave your present location unidentified (don't forget time zones — this is the indicator that may readily pinpoint your location)
Everything is quite straight-forward here, so let's get down to the interesting stuff: what are the advantages of utilizing your own service, and how should you go about establishing one?
Well, today you’re in for a treat — to answer these questions, we’ve put together a checklist with step-by-step instructions for setting up and configuring a VPN server.
Advantages of Using a Personal VPN Server
1. Bypassing blocks
Several countries attempt to fight VPNs by blocking them. But, if you use your own VPN, it will not appear in the main list of providers and will almost surely avoid blocks.
2. There are no captchas
All well-known services will request that you choose horses from a set of photographs, locate traffic lights, or identify a word in a picture. Why is this the case? Several others are using a ready-made VPN server at the same time as we are. Consequently, the website will suspect such traffic and assault you with captchas. When you use your own VPN server, however, this problem is avoided since you will have a unique IP address that will look like an ordinary user.
3. High speed
Off-the-shelf VPN servers often have low bandwidth since they typically don't have time to grow their servers and networks for a big number of customers. With a self-hosted resource, you’ll have all the bandwidth you could possibly need.
4. The ability to send all computer traffic through a VPN, not just browser traffic
5. No need to install third-party software
As you can see, having your own server solves the majority of the problems associated with using a VPN.
Checklist for creating your own VPN server
Take the example of DigitalOcean and its Droplet server.
Registration
If you already have a DigitalOcean account, you may go to the next stage. If not, you must first register (all the steps are intuitive, don’t worry).
Create a new Droplet that will function as a VPN server
Choose a data center from which you intend to connect to the internet. I selected to work with Frankfurt since it is physically closer to my country of residency, which improves working speed.
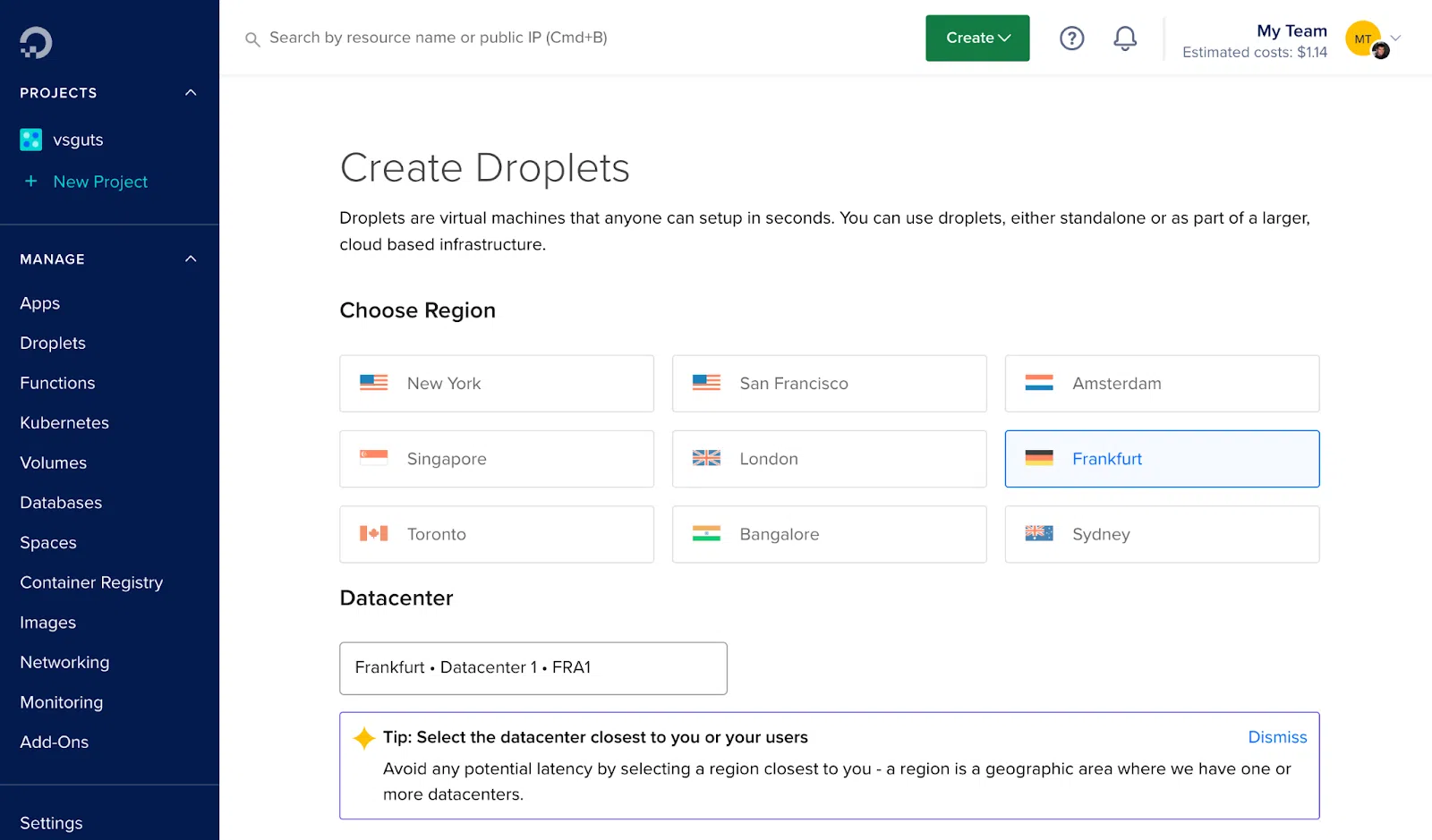
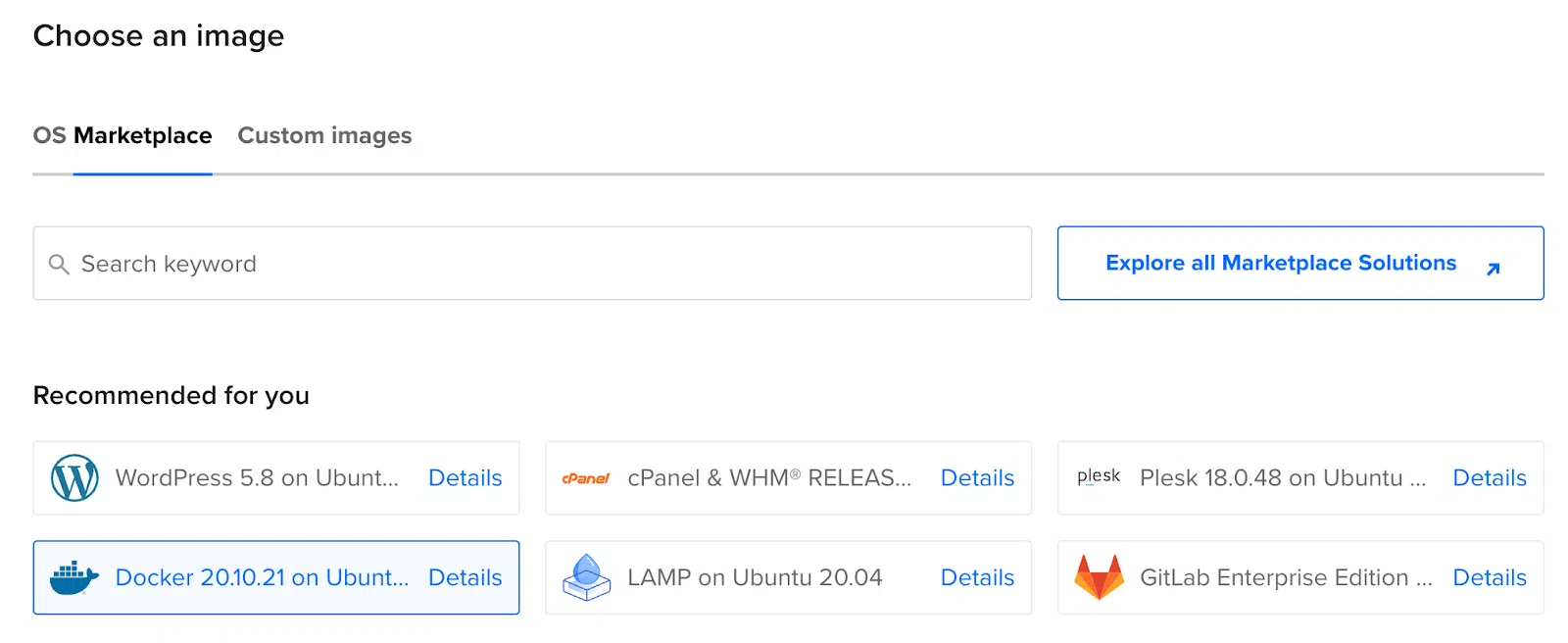
Choose Marketplace, and Docker on Ubuntu in the Image column. Finally, in the Size column, choose the subscription plan that suits you.
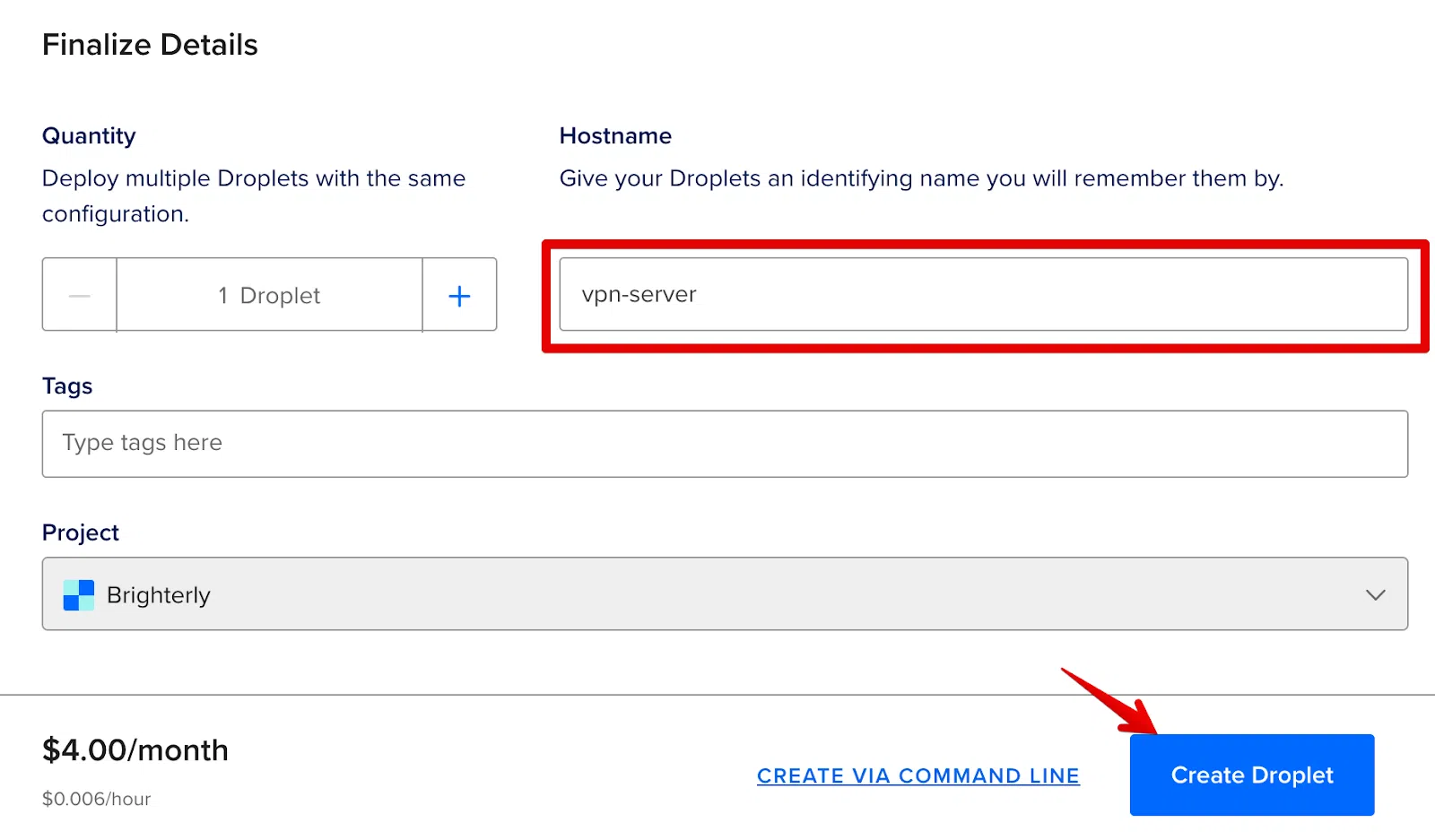
Next, put a name in Hostname, such as ‘vpn-server’. This has no effect and is simply for your convenience. Next, click the Create Droplet button.
Wait for the server to be created. This might take up to a minute. Following that, you will be given your server's IP address.
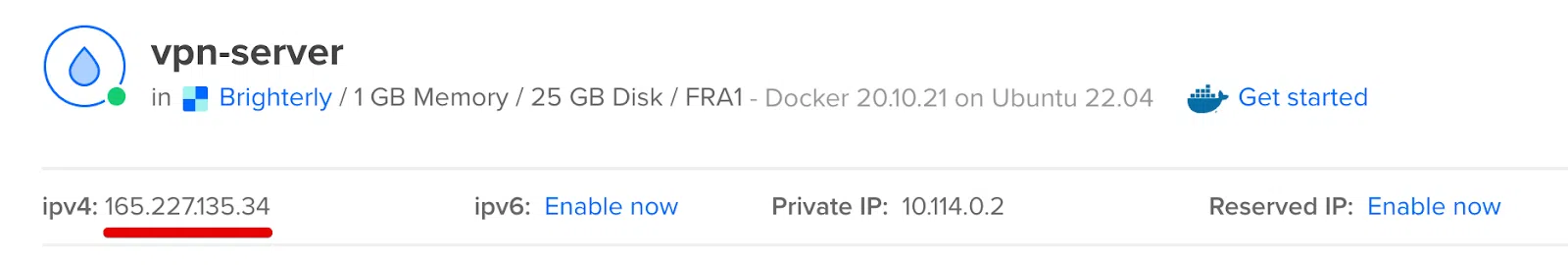
Connect to the SSH server
Launch Terminal on MacOS/Linux (or PowerShell/putty on Windows) and connect to our server through SSH using the root username and the IP address of our server.
This can be done with the help of:
ssh root@{your-ip-address}
> enter your password
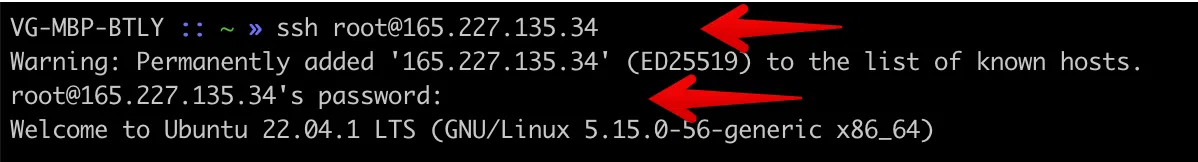
After that, you have to connect.
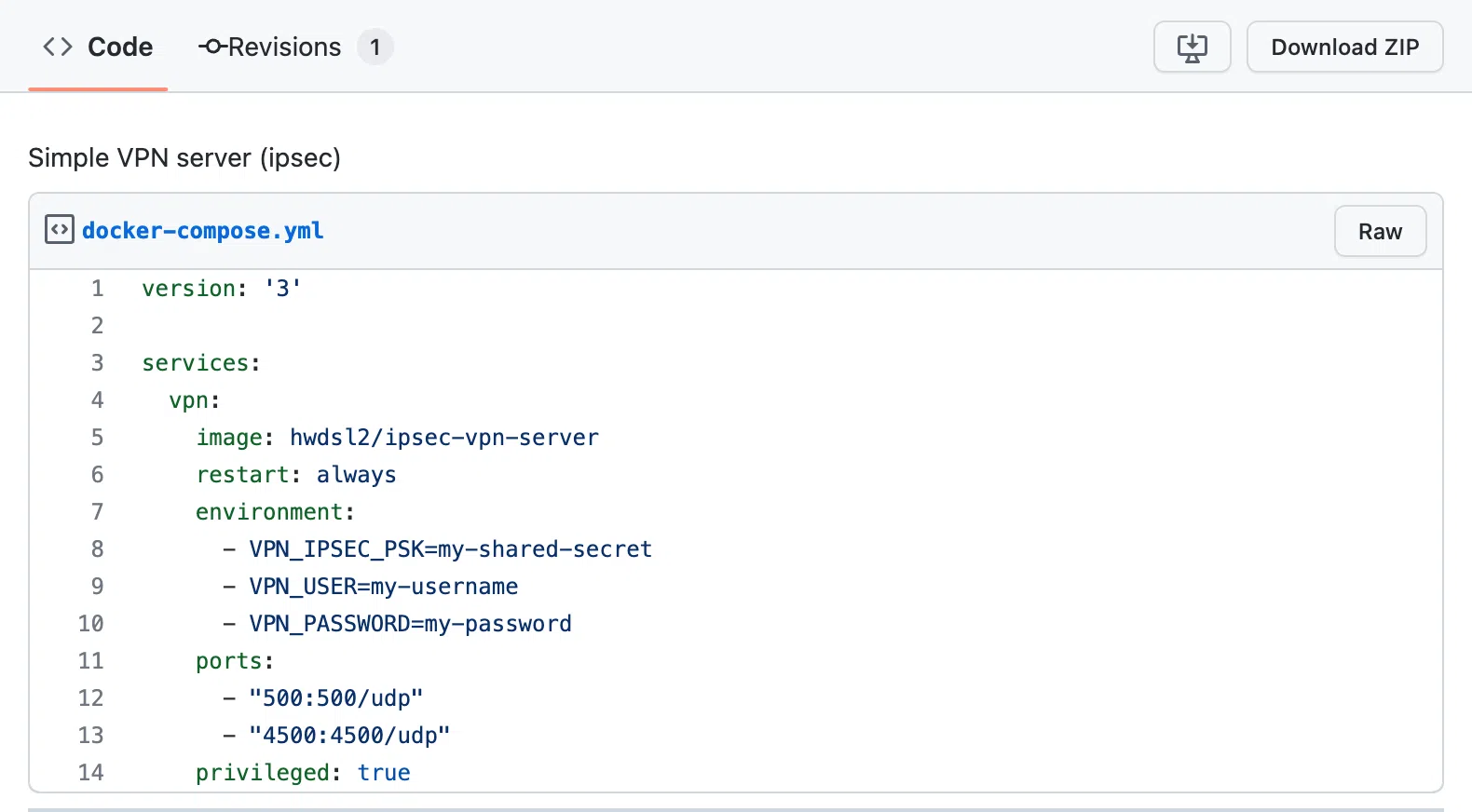
Create a docker-compose.yml file
Just copy the code from this website and paste it into your file. This is your server configuration file.
You may create a file directly over SSH using console text editors (nano/vim) or with an SFTP client. I used SSH to access the console editor.
In the same SSH window, input the following:
> nano docker-compose.yml
Paste the content. In the added text, change the following parameters for yourself:
• my-shared-secret — your secret word
• my-username — your personal login
• my-password — your password
Take note of how straightforward it is — there are just 14 lines in the file that we want.
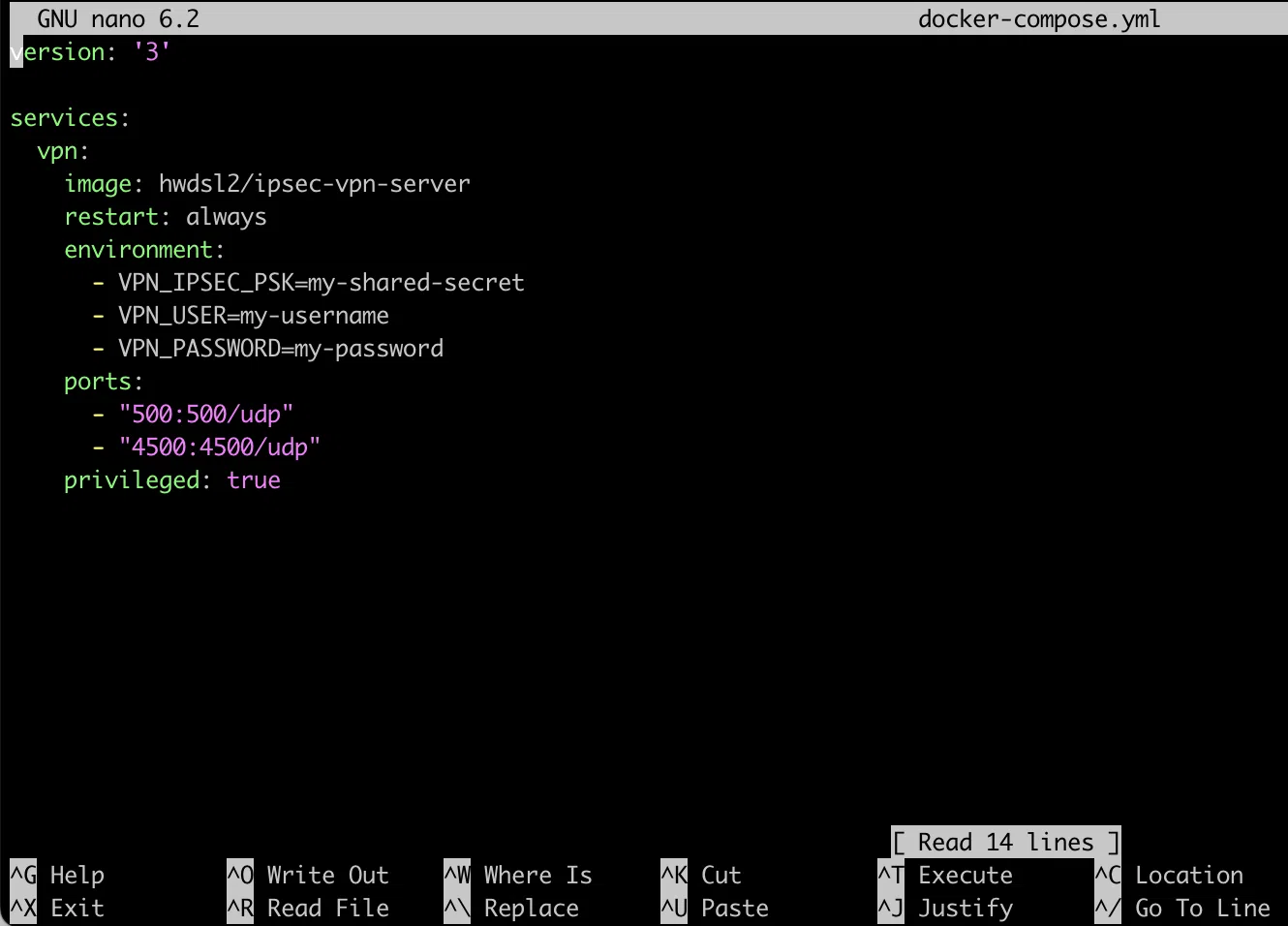
Exit by pressing Ctrl+X, then Y, and then press Enter.
Run the container with the recently created server
Use the same SSH window in which we just created the file.
> docker compose up -d
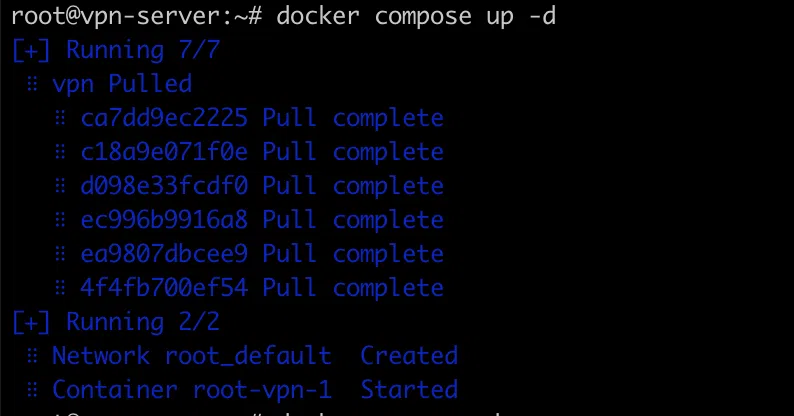
Congratulations! Your VPN server is up and running. So, how do you connect it?
Connect to the created VPN server
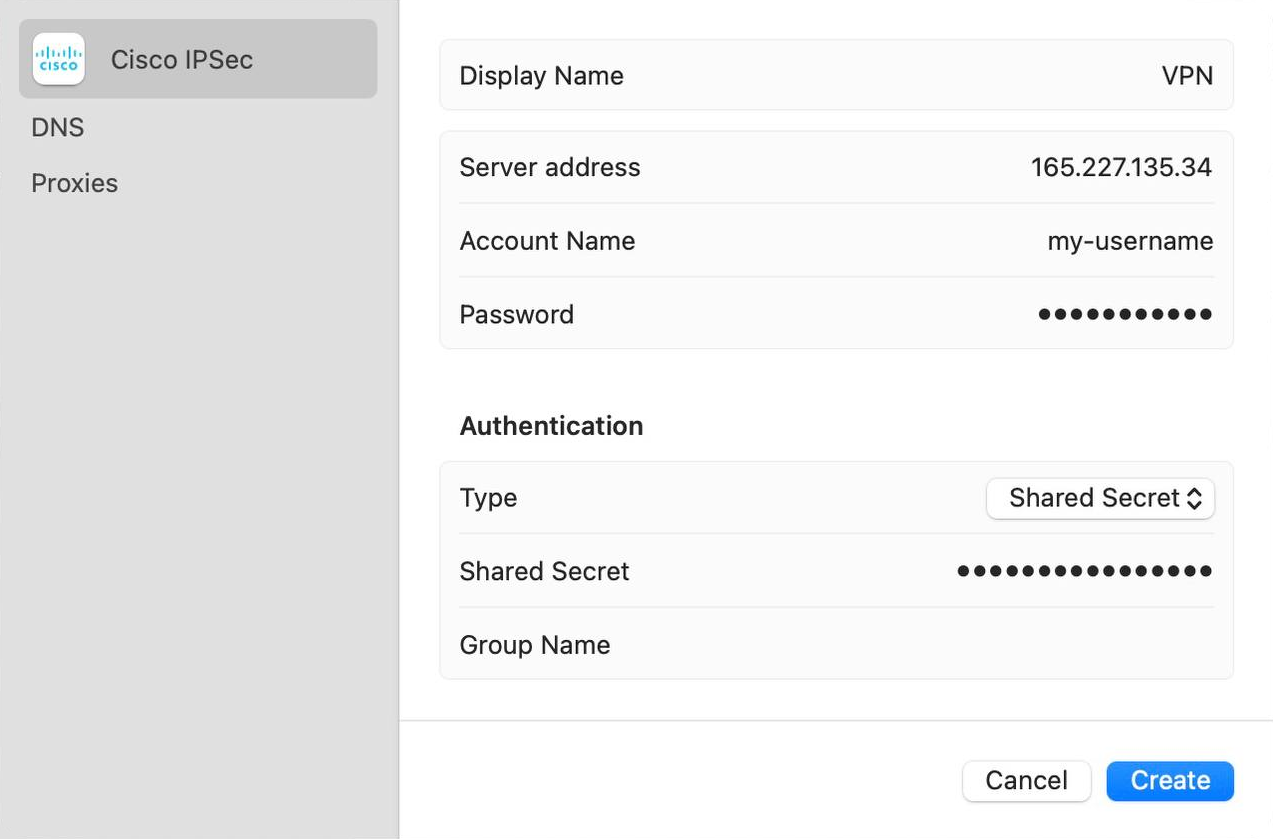
We recommend using IPsec because the clients for this VPN are already built into MacOS/Windows and you don't have to install anything locally. You just need to create a new VPN connection with the following parameters:
• Type: IPSec
• Server address: enter the IP address of the server
• Account name: write my-username (or the one you changed it to)
• Password: add my-password (or the one you changed it to)
• Shared Secret: write my-shared-secret (or the variant you changed earlier)
For MacOS, you don't need to install anything, just configure it like this:
For Windows, these settings will look a little different:
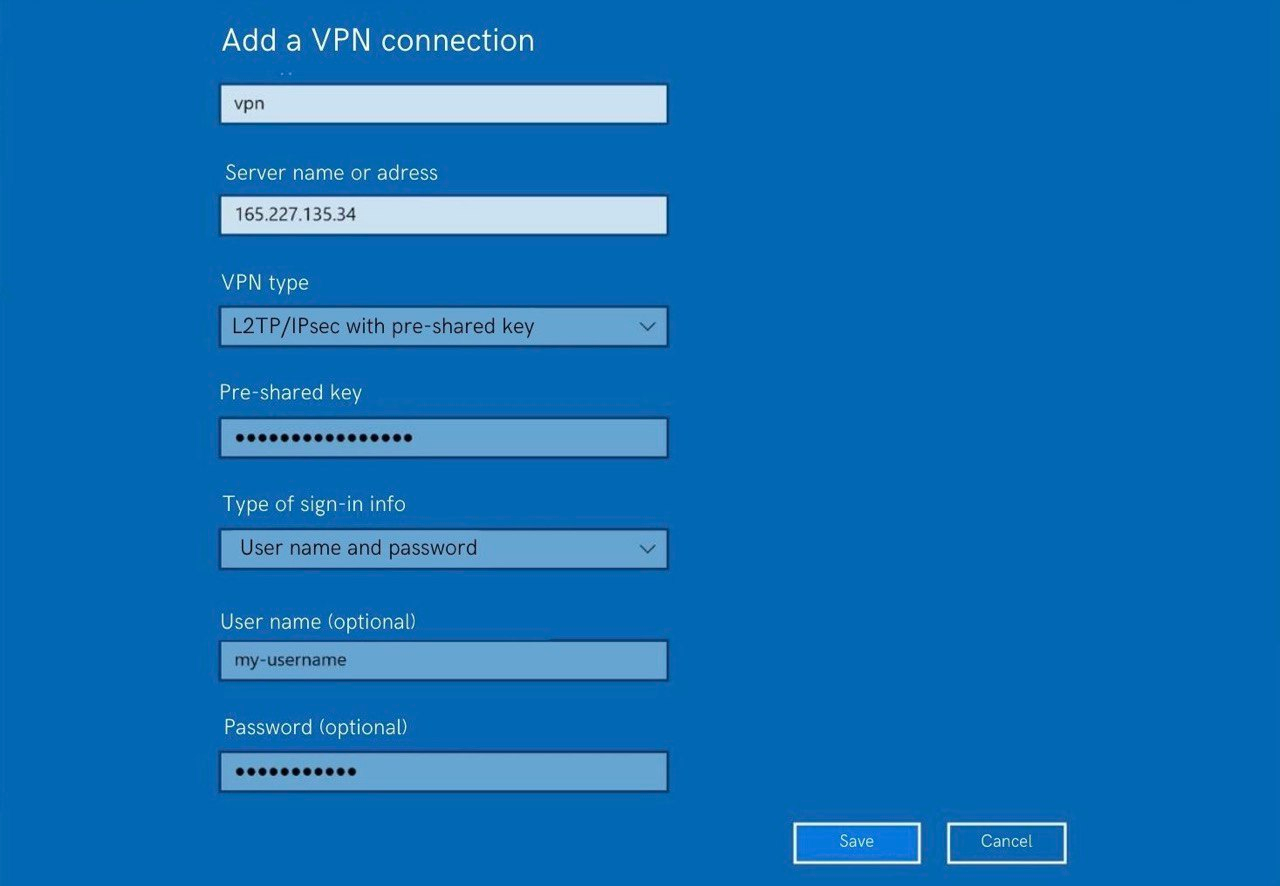
Unfortunately, Windows is not so simple and you will have to surf the registry and allow NAT-T.
For Linux users, there is also a screenshot with the required settings (I used them in Ubuntu 22.04):
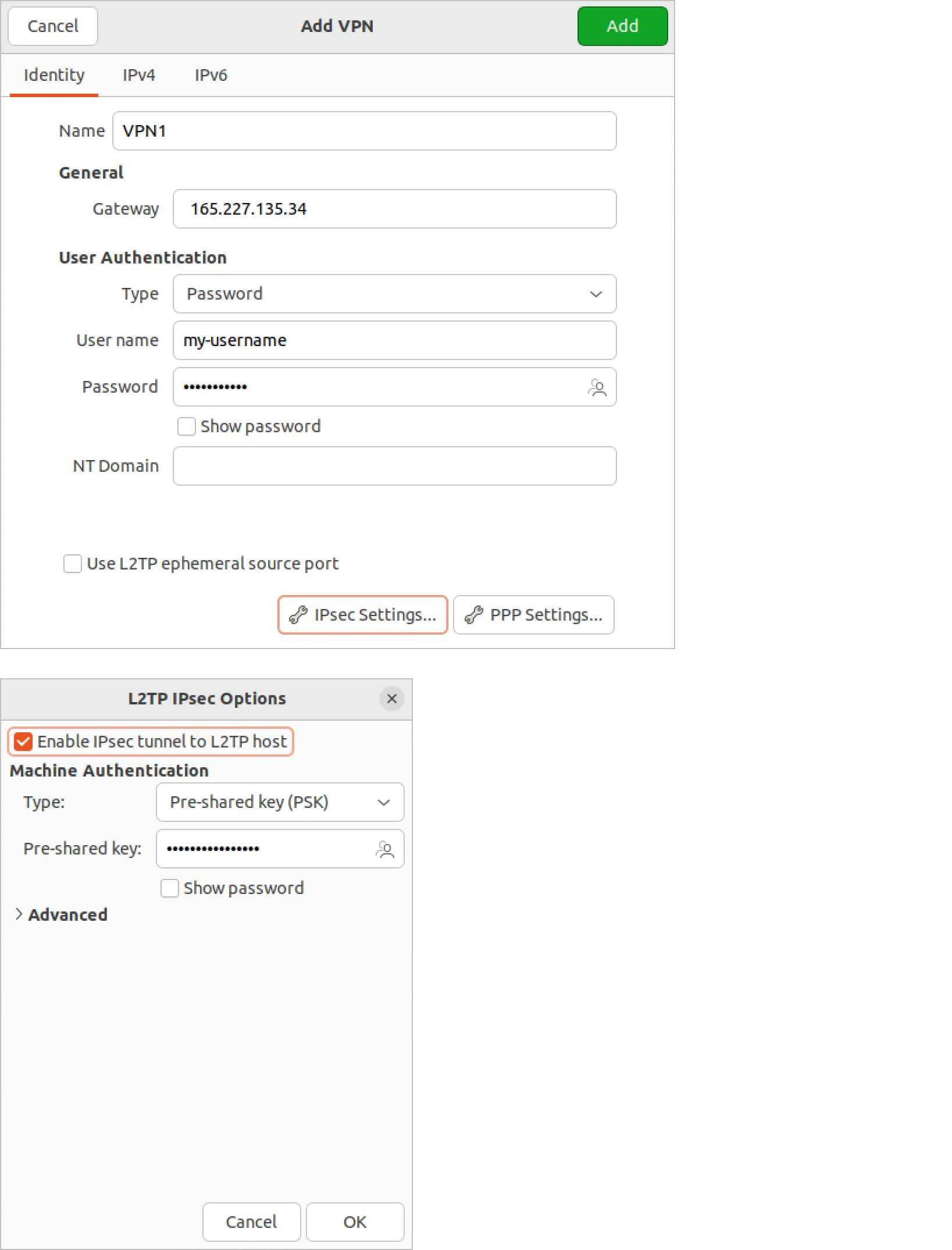
Before setting up, you need to install the network-manager-l2tp-gnome package. This is done through the console:
> sudo apt-get install network-manager-l2tp-gnome
You can also connect from your phone, you don't need to install anything else. The settings on the iPhone look like this:
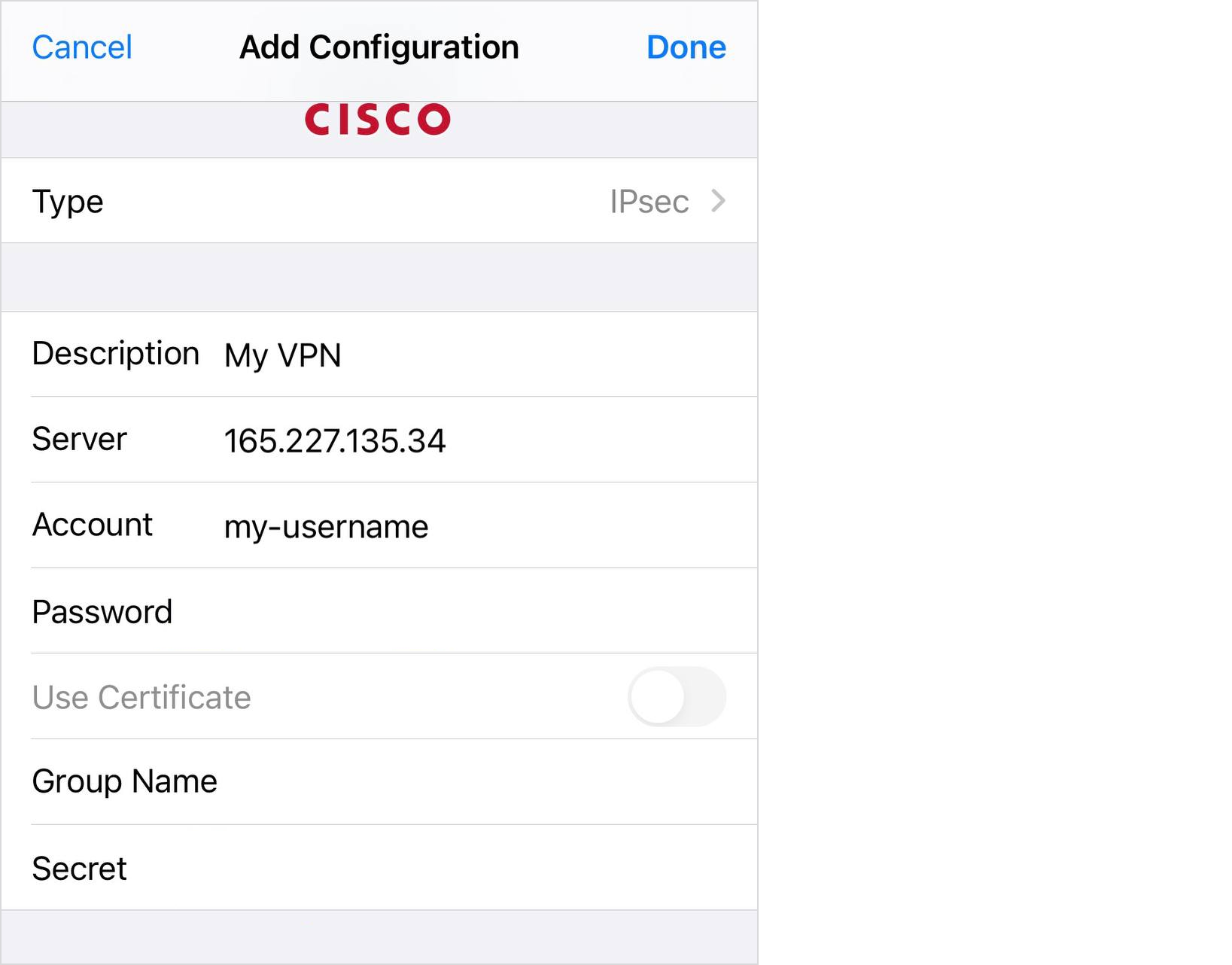
And that’s it — you're done! Connect and check the IP address, for example, on Whoer via the link. Now, for the whole Internet, you are physically located in the region where you created your VPN server, and the IP is the IP of the server. It's not as scary, time-consuming, or expensive as you might think.
Security recommendations
When it comes to the security of your server, I would, as a final thought, recommend:
• Using an SSH key instead of a password
• Changing the SSH-port from 22 to any other
• Using a complex password and Shared-secret (preferably a randomly generated string)
